パラチフス熱
出典: フリー百科事典『ウィキペディア(Wikipedia)』 (2018/12/31 04:29 UTC 版)
ナビゲーションに移動 検索に移動| Paratyphoid fever | |
|---|---|
| 別称 | Paratyphoid |
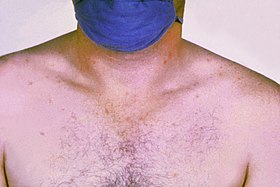 | |
| Rose colored spots on the chest of a person with typhoid fever which are similar to those of paratyphoid | |
| 診療科 | {{ Infectious disease }} |
| 症候学 | Fever, headache, rash, weakness[1][2] |
| 通常の発症 | 6–30 days post exposure[1][3] |
| 継続期間 | Weeks to months[1] |
| 原因 | Salmonella enterica spread by food or water contaminated with feces[1] |
| リスクファクター | Poor sanitation, crowded populations[4] |
| 診断法 | Culturing the bacteria or detecting its DNA in the blood, stool, or bone marrow[1][3] |
| 予防 | Handwashing, clean water[1] |
| 治療 | Antibiotics[1] |
| 頻度 | 529,000[5] |
| 死亡者数 | 29,200[6] |
パラチフスは腸管や血液中に生息する血清型Paratyphi AのSalmonella enterica細菌が原因でおこる[1]。 Paratyphi B、Paratyphi C による感染症はパラチフスから除外されサルモネラ症と改められた。 その感染経路は感染したヒトの糞に汚染された水や食へ物を口にすることである[1]。また、感染者が調理したものを食べることによって感染する場合もある[2]。リスク要因としては貧困人口の密集した不衛生な環境である[4]。稀に性行為によって感染することもある[1]。動物の中ではヒトだけに感染する[1]。診断方法は菌の培養、血や血便からの細菌のDNA、骨髄の検査で確認される[1][3]。菌の培養は困難な場合がある[3]。骨髄検査は最も正確な診断方法である[4]。パラチフスの症状は他の多くの感染症と似ている[3]。チフスはパラチフスとは関係のない病気である[8]。
パラチフス専用のワクチンはないが、腸チフスワクチンで多少の効果が得られることもある[1][2]。予防には清潔な飲料水、衛生環境、正しい手洗いである[1]。治療は抗生物質のアジスロマイシンを用いる[1]。一般的に従来のいくつかの抗生物質に対しては抵抗し効果がない[1]。
パラチフスは年間で約6万人に影響を及ぼしている[1][9]。一般的にアジアの地域でよく診られるが、先進国では稀である[1][2]。多くの場合はParatyphi BやCよりParatyphi Aにるよものである[3]。2015年のパラチフス熱による死亡者数は約29,200人、1990年は約63,000人である[10][6]。治療しなかった場合の死亡リスクは10%から15%、治療した場合は1%以下である[3]。
| ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w Anna E. Newton (2014). “3 Infectious Diseases Related To Travel”. CDC health information for international travel 2014 : the yellow book. ISBN 9780199948499. オリジナルの2015-07-02時点によるアーカイブ。.
- ^ a b c d e Jeremy Hawker (2012). “3.56”. Communicable disease control and health protection handbook (3rd ed.). Chichester, West Sussex, UK: Wiley-Blackwell. ISBN 9781444346947. オリジナルの2017-09-08時点によるアーカイブ。.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Alan J. Magill (2013). Hunter's tropical medicine and emerging infectious diseases (9th ed.). London: Saunders/Elsevier. pp. 568–572. ISBN 9781455740437. オリジナルの2017-09-08時点によるアーカイブ。.
- ^ a b c Crump, JA; Mintz, ED (2010年1月15日). “Global trends in typhoid and paratyphoid Fever.”. Clinical Infectious Diseases 50 (2): 241–6. doi:10.1086/649541. PMC 2798017. PMID 20014951.
- ^ GBD 2015 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence, Collaborators. (2016年10月8日). “Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 310 diseases and injuries, 1990-2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015.”. Lancet 388 (10053): 1545–1602. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31678-6. PMC 5055577. PMID 27733282.
- ^ a b GBD 2015 Mortality and Causes of Death, Collaborators. (2016年10月8日). “Global, regional, and national life expectancy, all-cause mortality, and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes of death, 1980-2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015.”. Lancet 388 (10053): 1459–1544. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(16)31012-1. PMID 27733281.
- ^ Wain, J; Hendriksen, RS; Mikoleit, ML; Keddy, KH; Ochiai, RL (2015年3月21日). “Typhoid fever.”. Lancet 385 (9973): 1136–45. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(13)62708-7. PMID 25458731.
- ^ Cunha BA (2004年3月). “Osler on typhoid fever: differentiating typhoid from typhus and malaria”. Infect. Dis. Clin. North Am. 18 (1): 111–25. doi:10.1016/S0891-5520(03)00094-1. PMID 15081508.
- ^ Global Burden of Disease Study 2013, Collaborators (2015年8月22日). “Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 301 acute and chronic diseases and injuries in 188 countries, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013.”. Lancet 386 (9995): 743–800. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(15)60692-4. PMC 4561509. PMID 26063472.
- ^ GBD 2013 Mortality and Causes of Death, Collaborators (2014年12月17日). “Global, regional, and national age-sex specific all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013.”. Lancet 385 (9963): 117–71. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61682-2. PMC 4340604. PMID 25530442.
- 1 パラチフス熱とは
- 2 パラチフス熱の概要
- パラチフス熱のページへのリンク
