ギダゼパム
ギダゼパム
出典: フリー百科事典『ウィキペディア(Wikipedia)』 (2025/05/04 01:03 UTC 版)
 |
|
 |
|
| IUPAC命名法による物質名 | |
|---|---|
|
|
| 臨床データ | |
| 販売名 | Gidazepam IC |
| 法的規制 |
|
| 薬物動態データ | |
| 代謝 | Hepatic |
| 半減期 | ~87 hours |
| 排泄 | Renal |
| データベースID | |
| CAS番号 |
129186-29-4 |
| PubChem | CID: 121919 |
| DrugBank | ?  |
| ChemSpider | 108764  |
| UNII | XMJ87I93Y9  |
| 化学的データ | |
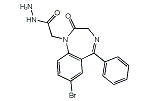
| 化学式 | |
| 分子量 | 387.24 g·mol−1 |
|
|
|
|
|
ギダゼパム(英:Gidazepam)はhydazepamまたはhidazepam[2]としても知られる、ソビエト連邦で開発された非定型ベンゾジアゼピン誘導体である薬物である[3][4]。 選択的抗不安薬としての作用を示すベンゾジアゼピン系薬物である[5]。また、特定の心血管障害の管理にも治療的効果がある[6][7][8][9][10]。
薬理学
ギダゼパムとその類似体のいくつかは、他のベンゾジアゼピンとは対照的に、ベンゾジアゼピン受容体よりもTSPO(以前は末梢ベンゾジアゼピン受容体)に対する選択的作動薬である[5]。
ギダゼパムは、その活性代謝物である7-ブロモ-2,3-ジヒドロ-5-フェニル-1H-1,4-ベンゾジアゼピン-2-オン(脱アルキルギダゼパムまたはブロモ-ノルダゼパム)のプロドラッグとして作用する[[11][12]。抗不安作用が発現するまでに数時間かかることがあるが、これはおそらく代謝が遅いためである(半減期87時間)。抗不安作用の発現と強さは、デサルキルギダゼパムの血中濃度と相関する[13]。

関連記事
- フェナゼパム—ロシアおよび他のCIS諸国で広く使用されているベンゾジアゼピン系薬物
- シナゼパム
- クロキサゾラム
- en:List of Russian drugs
脚注
- ^ https://mozdocs.kiev.ua/likiview.php?id=33305 "Категорія відпуску. За рецептом."/"Leave Status: By Prescription"
- ^ Library of Congress (2006). Library of Congress Subject Headings. Library of Congress. pp. 3300–
- ^ “[The new Soviet tranquilizer--gidazepam]”. Fel'dsher I Akusherka 56 (9): 35–7. (September 1991). PMID 1684941.
- ^ “[Experimental and clinical rationale for complex treatment of mental disorders in clean-up workers of the Chernobyl nuclear plant accident]”. Eksperimental'naia i Klinicheskaia Farmakologiia 65 (2): 12–6. (Mar 2002). PMID 12109283.
- ^ a b “Affinities of gidazepam and its analogs for mitochondrial benzodiazepine receptors”. Journal of Receptor and Signal Transduction Research 22 (1–4): 411–20. (Feb 2002). doi:10.1081/RRS-120014610. PMID 12503630.
- ^ “[The effect of gidazepam on the cardiovascular system function in patients with neurotic reactions and in healthy subjects under aggravated conditions]”. Eksperimental'naia i Klinicheskaia Farmakologiia 61 (1): 30–2. (Jan 1998). PMID 9575408.
- ^ “[The neuroregulatory modulation of the hemodynamic reactions to physical loading in patients with cardiac arrhythmias]”. Terapevticheskii Arkhiv 66 (9): 65–8. (1994). PMID 7992218.
- ^ “[New pharmacodynamic effects of gidazepam and befol in patients with cardiac arrhythmias]”. Eksperimental'naia i Klinicheskaia Farmakologiia 56 (5): 23–7. (Sep 1993). PMID 7906171.
- ^ “[Comparative analysis of antiarrhythmic action and electrophysiological effects of a new benzodiazepine derivative gidazepam and ethacizin in arrhythmias of various genesis]”. Kardiologiia 32 (6): 35–7. (June 1992). PMID 1405290.
- ^ “[Comparative anti-arrhythmia effectiveness of activators of body stress-limiting systems in patients with arrhythmia]”. Kardiologiia 32 (4): 25–30. (April 1992). PMID 1328745.
- ^ “[Biokinetics of a new prodrug gidazepam and its metabolite]”. Biulleten' Eksperimental'noi Biologii I Meditsiny 113 (1): 45–7. (January 1992). PMID 1356504.
- ^ “[Gidazepam biotransformation and pharmacokinetics in different species of animals and man]”. Eksperimental'naia i Klinicheskaia Farmakologiia 56 (3): 48–50. (May 1993). PMID 8106054.
- ^ “[The pharmacokinetic aspects of the clinical action of gidazepam]”. Eksperimental'naia i Klinicheskaia Farmakologiia 56 (3): 50–2. (May 1993). PMID 8106055.
- ギダゼパムのページへのリンク