シロシュモクザメ
| |||||||||||||||||||||
シロシュモクザメ
出典: フリー百科事典『ウィキペディア(Wikipedia)』 (2024/01/15 14:52 UTC 版)
| シロシュモクザメ | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| 保全状況評価[1] | |||||||||||||||||||||
| VULNERABLE (IUCN Red List Ver.3.1 (2001))  |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| 分類 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| 学名 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Sphyrna zygaena (Linnaeus, 1758) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| シノニム | |||||||||||||||||||||
* は不明確なシノニム |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| 英名 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Smooth hammerhead | |||||||||||||||||||||

分布
|
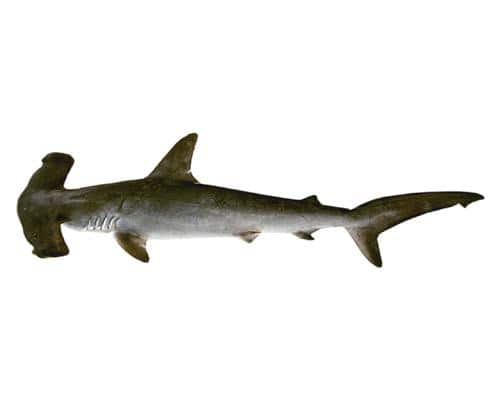
シロシュモクザメ (白撞木鮫、Sphyrna zygaena) はシュモクザメ科に属するサメの一種。ハンマー型の頭部(”cephalofoil”)の前縁に凹みがないことで他の大型シュモクザメと区別できる。全世界の温帯域に分布することも特徴であり、大きな群れを作って南北に季節回遊を行う。
シュモクザメとしてはヒラシュモクザメに次ぐ大きさで、全長4mに達する。活発な捕食者で硬骨魚や無脊椎動物を食べる。大型個体はサメやエイを食べることもある。胎生で、産仔数は20-40。人に対して潜在的に危険である。世界各地で漁獲され、特にフカヒレは最高級とされる。IUCNは保全状況を危急種としている。
分類
カール・フォン・リンネによって、1758年の『自然の体系』第10版において、Squalus zygaena の名で記載された。タイプ標本は指定されなかった。学名はその後 Sphyrna zygaena に変更された[2]。種小名 zygaena はギリシャ語の zygòn(くびき)に由来し、頭部の形に因んだものである[3]。この語は zýgaina という形で、アリストテレスの動物誌においてシュモクザメ類を指して用いられたこともある[4]。他の英名としてはcommon hammerhead・common smooth hammerhead・round-headed hammerhead、または単にhammerheadと呼ばれることもある.[5]。
形態系統解析からは、ヒラシュモクザメ・アカシュモクザメとともにシュモクザメ類で最も派生的なグループだと考えられていた。だが、核DNA・mtDNAを用いた分子系統解析では、本種はヒラシュモクザメとともにシュモクザメ属の中で最も基底的なグループを構成し、次に分岐したアカシュモクザメとは近縁でないという結果が得られている[6][7]。
形態

シュモクザメ類の中ではヒラシュモクザメ、アカシュモクザメに次いで大きく、通常は2.5-3.5mだが、最大で4m、重量では400kgに達する[8]。他の大型シュモクザメとはcephalofoilの形状が異なっており、中央に凹みがない。(大型のものでは微妙に凹んでいるものも存在する。)英名の"Smooth"もこの特徴に由来する。cephalofoilは全長の26–29%になる。鼻孔はcephalofoilの先端近くに位置し、長い溝が前縁を中央に向かって走る。歯列は上顎で26–32、下顎で25–30。各歯は三角形で、縁は滑らかか僅かに鋸歯状になる[8]。
体は流線型で、2基の背鰭の間に隆起線はない。第一背鰭はある程度高くて鎌型、先端は丸い。胸鰭・腹鰭は鎌型にならず、後縁はほぼ直線である。臀鰭は第二背鰭より大きく、後縁には強い欠刻があり、後端は長く伸びる[2]。皮歯は密に詰まる。各皮歯には5–7本(幼体では3本)の水平の隆起線があり、W字型をした後縁に続く。背面は暗い灰褐色から緑褐色だが、他のシュモクザメと異なり体側は明るい色になる。腹面は白。胸鰭の下側の縁は黒くなることがある[8]。
分布
シュモクザメの中では最も低温に耐えることができ、他のシュモクザメより高緯度で見られる。西部大西洋では、ノバスコシア州からヴァージン諸島とブラジルからアルゼンチン南部。東部大西洋では、ブリテン諸島からコートジボワール・地中海。インド洋では南アフリカ・インド・スリランカ。西部太平洋ではトンキン湾から日本南部・シベリア、オーストラリア・ニュージーランド。中部-東部太平洋では、ハワイ・カリフォルニア州・パナマ・ガラパゴス諸島・エクアドル・チリに分布する。一般的に熱帯には生息しないが、インドのマンナール湾やモザンビーク南部からも稀に報告がある。熱帯域では本種は他のシュモクザメと混同されていると考えられ、実際に熱帯域に生息するかどうかを判断するのは難しい[2]。
200m程度まで潜ることはあるが、アカシュモクザメ・ヒラシュモクザメに比べ、本種は深度20mより上の海面近くに留まる傾向がある。沿岸近くの湾内や河口域を好み、稀に大陸棚上の外洋や海洋島で見られる。フロリダ州のインディアン川などで、淡水に入ることも報告されている。回遊を行い、夏には高緯度に、冬には低緯度に移動する[9]。
生態

成体は単独、または小さい群れで過ごす。回遊時には巨大な群れを作ることもあり、東ケープ州では1.5m以下の幼体による100匹以上の群れが、カリフォルニア州では数千匹の群れが観察されている[2][9]。暑い夏には海面直下を、背鰭を海面から突き出して泳ぐ姿が見られる[8]。幼体はドタブカなどの大型のサメに捕食され[8]、成体はニュージーランド沖でシャチに捕食される姿が観察されている[10]。寄生虫として線虫の Parascarophis sphyrnae ・Contracaecum spp. が知られている[8]。
活動的な捕食者で、硬骨魚・軟骨魚・頭足類などを捕食し、共食いも行う。稀にエビ・カニ・フジツボなどの甲殻類を食べることもある。釣り針に掛かった魚を奪い取ることもよくある[2]。アカエイ科のエイが主な獲物として好まれている地域もあり、エイの尾にある毒針が口の周りに刺さっている個体もよく見られる。ある個体では95本の棘が刺さっていた[11]。ヨーロッパ北部ではタイセイヨウニシンやヨーロッパスズキ、北アメリカではサワラ属のScomberomorus maculatus やスミツキニシン属を食べる[8]。南アフリカでは大陸棚の縁の深いサンゴ礁に生息し、ヨーロッパヤリイカのようなイカやイワシ類などの群泳する小魚を食べる。2mを超える個体では、小型の軟骨魚類を獲物とする率が増える。オーストラリアではイカが主要な獲物で、硬骨魚がそれに続く[12][13]。
他のシュモクザメ同様に胎生で、卵黄を使い果たした胎児は卵黄嚢を胎盤に転換する。妊娠期間は10-11ヶ月。産仔数は20-50で比較的多い[9]。出産はサウスカロライナ州のブルズ湾のような、成育場となる沿岸の浅瀬で行われる[14]。出生時は50-61cm。地域によって差はあるが、雌は2.7m、雄は2.1-2.5mで性成熟する[8]。南アフリカでは、交尾を済ませた雌が2月に、臨月の雌が11月に捕獲されている。オーストラリア東部では出産は1-3月で、排卵もこれと同時期に起こる[12]。20年以上生きると考えられている[8]。
人との関わり
潜在的に危険であると考えられる。2008年の国際サメ被害目録には大型シュモクザメによる34件の攻撃が記録されており、その内17件が能動的な攻撃例がある[15]。だが、本種は他のシュモクザメより高緯度に生息するために、遊泳者と遭遇する確率も低く、これらの攻撃への寄与は小さいと考えられる[8]。カリフォルニア南部では、釣り人やダイバーが捕まえた魚を奪い取ったことが報告されている[2]。
米国の東・西海岸、ブラジル・スペイン・台湾・フィリピン・オーストラリア南西部・西アフリカなど全世界において、主に刺し網と延縄によって本種に対する商業漁業が行われている。他の大型シュモクザメと混同されて扱われるため、漁獲量を推定することは難しい[12]。肉は生・干物・塩漬け・燻製で販売されるが、中毒の報告があるためほとんどの市場において消費は望ましくないと考えられる。鰭はふかひれとして最高級に位置付けられるため、フィニングが行われることもある。肝油・鮫皮・魚粉などに利用されることもある[8]。漢方薬としても扱われる[5]。
また、他の魚種を対象とした漁業によっても混獲されており、遊漁者も本種を標的とすることがある。海水浴客を保護するためのサメよけネットに絡まって死亡する個体もいる。南アフリカのクワズール・ナタール州では、1978–1990年にこのネットによる死亡は年間10個体以下だったが、対照的にオーストラリアのニューサウスウェールズ州では、1972–1990年に死亡した4,715匹の内50%が本種だった[12]。現在はまだ、本種は比較的普通種であるが、IUCNは保全状況を危急種としている[1]。ニュージーランドでは漁獲が禁止されており、北西部沿岸では最も豊富なサメである。また、オーストラリア南部の漁業によっても悪影響は受けていないようである[8]。米国東海岸では、アメリカ海洋漁業局 (NMFS) によって大型の沿岸性サメ (Large Coastal Shark, LCS) と分類され、大西洋のサメ類に対する漁業管理計画によって捕獲が規制されている[12]。2013年、本種は他の大型板鰓類とともにCITESの附属書IIに掲載され、漁業と取引はライセンスと規制の下で行われることとなった[16]。
脚注
- ^ a b Casper, B.M., A. Domingo, N. Gaibor, M.R. Heupel, E. Kotas, A.F. Lamónaca, J.C. Pérez-Jimenez, C. Simpfendorfer, W.D. Smith, J.D. Stevens, A. Soldo, and C.M. Vooren (2005). "Sphyrna zygaena". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2008. International Union for Conservation of Nature. 2010年3月6日閲覧。
- ^ a b c d e f Compagno, L.J.V. (1984). Sharks of the World: An Annotated and Illustrated Catalogue of Shark Species Known to Date. Rome: Food and Agricultural Organization. pp. 553–554. ISBN 92-5-101384-5
- ^ Ellis, R. (1989). The Book of Sharks. New York: Alfred A. Knopf Inc. ISBN 0-679-72210-6
- ^ Aristotle (350 BCE). History of Animals (Book II) chap. XI.11
- ^ a b Froese, Rainer and Pauly, Daniel, eds. (2008). "Sphyrna zygaena" in FishBase. January 2008 version.
- ^ Lim, D.D.; Motta, P.; Mara, K.; Martin, A.P. (2010). “Phylogeny of hammerhead sharks (Family Sphyrnidae) inferred from mitochondrial and nuclear genes”. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 55 (2): 572–579. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2010.01.037. PMID 20138218.
- ^ Cavalcanti, M.J. (2007). “A Phylogenetic Supertree of the Hammerhead Sharks (Carcharhiniformes: Sphyrnidae)”. Zoological Studies 46 (1): 6–11.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l Bester, C. Biological Profiles: Smooth Hammerhead. Florida Museum of Natural History Ichthyology Department. Retrieved on October 19, 2008.
- ^ a b c Ebert, D.A. (2003). Sharks, Rays, and Chimaeras of California. University of California Press. pp. 178–179. ISBN 0-520-23484-7
- ^ Visser, I.N. (January 2005). “First Observations of Feeding on Thresher (Alopias vulpinus) and Hammerhead (Sphyrna zygaena) Sharks by Killer Whales (Orcinus orca) Specialising on Elasmobranch Prey”. Aquatic Mammals 31 (1): 83–88. doi:10.1578/AM.31.1.2005.83.
- ^ Strong, W.R., Snelson, Jr., F.F., and Gruber, S.H. (September 19, 1990). “Hammerhead Shark Predation on Stingrays: An Observation of Prey Handling by Sphyrna mokarran”. Copeia (American Society of Ichthyologists and Herpetologists) 1990 (3): 836–840. doi:10.2307/1446449. JSTOR 1446449.
- ^ a b c d e Fowler, S.L., Cavanagh, R.D., Camhi, M., Burgess, G.H., Cailliet, G.M., Fordham, S.V., Simpfendorfer, C.A. and Musick, J.A. (2005). Sharks, Rays and Chimaeras: The Status of the Chondrichthyan Fishes. International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources. pp. 106–109, 318–320. ISBN 2-8317-0700-5
- ^ Smale, M.J. (December 1991). “Occurrence and feeding of three shark species, Carcharhinus brachyurus, C. obscurus and Sphyrna zygaena, on the Eastern Cape coast of South Africa”. South African Journal of Marine Science 11 (1): 31–42. doi:10.2989/025776191784287808.
- ^ Sumich, J.L. and Morrissey, J.F. (2004). Introduction to the Biology of Marine Life (eighth ed.). Jones & Bartlett Publishers. p. 197. ISBN 0-7637-3313-X
- ^ ISAF Statistics on Attacking Species of Shark. International Shark Attack File, Florida Museum of Natural History, University of Florida. Retrieved on May 18, 2009.
- ^ “CITES conference takes decisive action to halt decline of tropical timber, sharks, manta rays and a wide range of other plants and animals”. Cites. 2014年11月30日閲覧。
外部リンク
- シロシュモクザメのページへのリンク