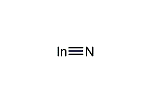窒化インジウム
窒化インジウム
出典: フリー百科事典『ウィキペディア(Wikipedia)』 (2025/11/02 23:34 UTC 版)

|
|
| 物質名 | |
|---|---|
|
別名
Indium(III) nitride |
|
| 識別情報 | |
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.042.831 |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 性質 | |
| InN | |
| モル質量 | 128.83 g/mol |
| 外観 | 黒色粉末 |
| 密度 | 6.81 g/cm3 |
| 融点 | 1,100 °C (2,010 °F; 1,370 K) |
| 加水分解 | |
| バンドギャップ | 0.65 eV (300 K) |
| 電子移動度 | 3200 cm2/(V.s) (300 K) |
| 熱伝導率 | 45 W/(m.K) (300 K) |
| 屈折率 (nD) | 2.9 |
| 構造 | |
| ウルツ鉱(六方晶) | |
| C46v-P63mc | |
|
a = 354.5 pm, c = 570.3 pm [1]
|
|
| 四面体 | |
| 危険性 | |
| 労働安全衛生 (OHS/OSH): | |
|
主な危険性
|
刺激性、アンモニアに加水分解 |
| 安全データシート (SDS) | External SDS |
| 関連する物質 | |
| その他の 陰イオン |
リン化インジウム ヒ化インジウム アンチモン化インジウム |
| その他の 陽イオン |
窒化ホウ素 窒化アルミニウム 窒化ガリウム |
| 関連物質 | 窒化インジウムガリウム 窒化インジウムガリウムアルミニウム |
|
特記無き場合、データは標準状態 (25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa) におけるものである。
|
|
窒化インジウム(ちっかインジウム、indium nitride)は、インジウムと窒素からなる化学式InNの半導体である。バンドギャップが小さく、太陽電池や高速エレクトロニクスに用いられる[2]。InNのバンドギャップは、現在では温度に応じ〜0.7 eVであることが分かっている[3](かつては1.97 eVとされていた)。有効電子静止質量は、高磁場での測定で[4][5]m*=0.055 m0と求められた。窒化ガリウムとの三元合金である窒化インジウムガリウム (InGaN) は、赤外線 (0.69 eV) から紫外線 (3.4 eV) の範囲の直接バンドギャップを持つ。
窒化物の半導体を用いた太陽電池の開発が進められている。InGaN合金を用いると、太陽のスペクトルに合ったものが得られる。InNのバンドギャップは、波長1900 nmまでを用いることを可能とするが、このような太陽電池が市販されるまでにはまだ多くの課題がある。p型ドープしたInNやインジウムの多いInGaNは、最大の挑戦の1つである。InNと窒化ガリウムや窒化アルミニウム等の他の窒化物とのヘテロエピタキシャル成長は難しいことが知られている。
InNの薄い多結晶フィルムは高い伝導性を示し、ヘリウム温度では超伝導にもなる。超伝導遷移温度Tcは、フィルムの構造に依存し、4 K以下となる[6][7]。わずか0.03テスラで超伝導性を失う金属インジウムとは異なり、超伝導性は数テスラの高磁場中でも持続する。それにもかかわらず、この超伝導性は、ギンツブルグ-ランダウ理論によると[8]金属インジウムのチェーン[6]またはナノクラスタが原因である。
出典
- ^ Pichugin, I. G.; Tlachala, M. (1978). “Rentgenovsky analiz nitrida indiya [X-ray analysis of indium nitride]” (Russian). Izvestiya Akademii Nauk SSSR: Neorganicheskie Materialy 14 (1): 175–176.
- ^ T. D. Veal, C. F. McConville, and W. J. Schaff (Eds), Indium Nitride and Related Alloys (CRC Press, 2009)
- ^ V. Yu. Davydov et al. (2002). “Absorption and Emission of Hexagonal InN. Evidence of Narrow Fundamental Band Gap” (free download pdf). Physica Status Solidi (b) 229: R1. Bibcode: 2002PSSBR.229....1D. doi:10.1002/1521-3951(200202)229:3<r1::aid-pssb99991>3.0.co;2-o.
- ^ Goiran, Michel,, (2010). “Electron cyclotron effective mass in indium nitride”. APPLIED PHYSICS LETTERS 96: 052117. Bibcode: 2010ApPhL..96e2117G. doi:10.1063/1.3304169.
- ^ Millot, Marius, (2011). “Determination of effective mass in InN by high-field oscillatory magnetoabsorption spectroscopy”. Phys. Rev. B 83: 125204. Bibcode: 2011PhRvB..83l5204M. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.83.125204.
- ^ a b T. Inushima (2006). “Electronic structure of superconducting InN” (free download pdf). Sci. Techn. Adv. Mater. 7 (S1): S112. Bibcode: 2006STAdM...7S.112I. doi:10.1016/j.stam.2006.05.009.
- ^ Tiras, E.; Gunes, M.; Balkan, N.; Airey, R.; Schaff, W. J. (2009). “Superconductivity in heavily compensated Mg-doped InN”. Applied Physics Letters 94 (14): 142108. Bibcode: 2009ApPhL..94n2108T. doi:10.1063/1.3116120.
- ^ Komissarova, T. A.; Parfeniev, R. V.; Ivanov, S. V. (2009). “Comment on "Superconductivity in heavily compensated Mg-doped InN" [Appl. Phys. Lett. 94, 142108 (2009)]”. Applied Physics Letters 95 (8): 086101. Bibcode: 2009ApPhL..95h6101K. doi:10.1063/1.3212864.
関連項目
外部リンク
- “Indium Nitride (InN)”. Ioffe Physico-Technical Institute. 2008年6月17日閲覧。
- 窒化インジウムのページへのリンク