スワインソニン
| 分子式: | C8H15NO3 |
| その他の名称: | スワインソニン、Swainsonine、(1S,2α,8β,8aβ)-Octahydro-1,2,8-indolizinetriol、(-)-スワインソニン、(-)-Swainsonine、(1S,8aβ)-Octahydroindolizine-1α,2α,8β-triol、(-)-D-スワインソニン、(-)-D-Swainsonine、D-スワインソニン、D-Swainsonine |
| 体系名: | (8aβ)-オクタヒドロインドリジン-1α,2α,8β-トリオール、(1S,2α,8β,8aβ)-オクタヒドロ-1,2,8-インドリジントリオール、(1S,8aβ)-オクタヒドロインドリジン-1α,2α,8β-トリオール |
L‐スワインソニン
スワインソニン
出典: フリー百科事典『ウィキペディア(Wikipedia)』 (2024/10/06 08:13 UTC 版)
| スワインソニン | |
|---|---|
 |
|
|
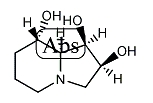
(1S,2R,8R,8aR)-1,2,3,5,6,7,8,8a-Octahydroindolizine- 1,2,8-triol |
|
|
別称
Tridolgosir
(−)-スワインソニン D-スワインソニン |
|
| 識別情報 | |
| CAS登録番号 | 72741-87-8 |
| PubChem | 51683 |
| 日化辞番号 | J12.698E |
| RTECS番号 | NM2408666 |
|
|
| 特性 | |
| 化学式 | C8H15NO3 |
| モル質量 | 173.21 g mol−1 |
| 融点 | 143-144 °C |
| 水への溶解度 | 10 mg/1 mL |
| 危険性 | |
| 安全データシート(外部リンク) | Sigma Aldrich |
| EU分類 |  X X |
| Rフレーズ | R20/21/22 |
| Sフレーズ | S36 |
| 特記なき場合、データは常温 (25 °C)・常圧 (100 kPa) におけるものである。 | |
スワインソニン(英: swainsonine)はインドリジジンアルカロイドの一種。ゴルジαマンノシダーゼIIの強力な阻害剤、免疫調整剤であり、化学療法の候補薬である。Locoweed(Loco: 狂う + Weed: 草)の主要な毒成分であり[1]、また特に北アメリカにおいて畜産業に深刻な経済的損失を与える原因となっている。
薬理学作用
スワインソニンはグリコシダーゼ、特にN-結合型グリコシル化を阻害する。スワインソニンによるゴルジαマンノシダーゼIIの阻害によりハイブリッド型グリカンが生成する。これらのグリカンはMan5GlcNAc2型のコア構造を持ち,いわゆる複雑型グリカンと類似している。
本化合物の薬理学作用は、いまだ不明な点が多い。
単離・生合成・合成
スワインソニンは数多くの被子植物および菌から単離される天然物であり、オーストラリアのマメ科Swainosona canescens (Benth.) A Leeから初めて単離された[2]。その他、Astragalus lentiginosus[3]やRhizoctonia leguminicola[4]からも単離されている。1982年にHextableらによって相対立体配置が提唱され[2]、1983年にHarrisらによって絶対立体配置が決定された[4]。スワインソニンは商業的にはメタリジウム(Metarhizium anisopliaeなどいくつかの植物および菌から抽出される他、全合成も多数報告されている[5]。
畜産業に対する影響
スワインソニンによる常習的な中毒により、家畜では様々な神経障害が引き起こされるため、スワインソニンを含む植物は "Locoweed" と総称される。その他の中毒による症状は、若い家畜では食欲減退や成長不良、大人の家畜では体重減少、また繁殖の停止(性欲、繁殖力の喪失や流産)である[6] 。これらの神経系の機能低下や筋肉に対する症状は、生化学的、形態学的、臨床的にマンノドーシスと類似している。
薬の候補として
スワインソニンは神経膠腫[7]や胃がん[8]の治療薬候補となっている。しかしながら、GD0039(スワインソニンの塩酸塩)の17人の腎臓がん患者に対する第II相臨床試験では、有望な結果は得られなかった[9]。スワインソニンの抗腫瘍活性はマクロファージの刺激に起因している[10]。
スワインソニンは抗がん剤の補助薬やその他の化学療法の候補化合物となっている。マウスでは、スワインソニンはドキソルビシンの毒性を軽減するため、スワインソニンとの併用によりドキソルビシンの用量を高めることが可能となることが示唆されている[11][12]。スワインソニンは抗がん治療による骨髄損傷からの回復を促進させる[13][14]。
また、食欲減退薬でもある[15]。
脚注
- ^ Stegelmeier BL, Molyneux RJ, Elbein AD, James LF (1995). “The lesions of locoweed (Astragalus mollissimus), swainsonine, and castanospermine in rats”. Veterinary Pathology 32 (3): 289–98. PMID 7604496.
- ^ a b “A Spectroscopic Investigation of Swainsonine: An α-Mannosidase Inhibitor Isolated from Swainsona canescens”. Aust. J. Chem. 32: 2257-2264. (1979). doi:10.1071/CH9792257.
- ^ Molyneux, Russell J and James, Lynn F (1982). “Loco intoxication: indolizidine alkaloids of spotted locoweed (Astragalus lentiginosus)”. Science (American Association for the Advancement of Science) 216 (4542): 190-191. doi:10.1126/science.6801763. PMID 6801763.
- ^ a b Schneider, M. J.; Ungemach, F. S.; Broquist, H. P.; Harris, T. M. (1983). “(1S,2R,8R,8aR)-1,2,8-trihydroxyoctahydroindolizine (swainsonine), an α-mannosidase inhibitor from Rhizoctonia leguminicola”. Tetrahedron 39 (1): 29-32. doi:10.1016/S0040-4020(01)97625-2.
- ^ Bates, R. W.; Dewey, M. R. (2009). “A Formal Synthesis of Swainsonine by Gold-Catalyzed Allene Cyclization”. Org. Lett. 11: 3706–3708. doi:10.1021/ol901094h. and references therein.
- ^ Panter KE, James LF, Stegelmeier BL, Ralphs MH, Pfister JA (1999). “Locoweeds: effects on reproduction in livestock”. J. Nat. Toxins 8 (1): 53–62. PMID 10091128.
- ^ Sun JY, Yang H, Miao S, Li JP, Wang SW, Zhu MZ, Xie YH, Wang JB, Liu Z, Yang Q (2009). “Suppressive effects of swainsonine on C6 glioma cell in vitro and in vivo”. Phytomedicine 16: 1070-1074. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2009.02.012. PMID 19427771.
- ^ Sun JY, Zhu MZ, Wang SW, Miao S, Xie YH, Wang JB (2007). “Inhibition of the growth of human gastric carcinoma in vivo and in vitro by swainsonine”. Phytomedicine 14 (5): 353–9. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2006.08.003. PMID 17097281.
- ^ Shaheen PE, Stadler W, Elson P, Knox J, Winquist E, Bukowski RM (2005). “Phase II study of the efficacy and safety of oral GD0039 in patients with locally advanced or metastatic renal cell carcinoma”. Investigational New Drugs 23 (6): 577–81. doi:10.1007/s10637-005-0793-z. PMID 16034517.
- ^ Das PC, Roberts JD, White SL, Olden K (1995). “Activation of resident tissue-specific macrophages by swainsonine”. Oncol. Res. 7 (9): 425–33. PMID 8835286.
- ^ Oredipe OA, Furbert-Harris PM, Laniyan I, Green WR, Griffin WM, Sridhar R (2003). “Mice primed with swainsonine are protected against doxorubicin-induced lethality”. Cellular and Molecular Biology (Noisy-le-Grand, France) 49 (7): 1089–99. PMID 14682391.
- ^ Oredipe OA, Furbert-Harris PM, Laniyan I, Green WR, Griffin WM, Sridhar R (2003). “Coadministration of swainsonine and doxorubicin attenuates doxorubicin-induced lethality in mice”. Cellular and Molecular Biology (Noisy-le-Grand, France) 49 (7): 1037–48. PMID 14682385.
- ^ Oredipe OA, Furbert-Harris PM, Laniyan I, Griffin WM, Sridhar R (2003). “Limits of stimulation of proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow cells of mice treated with swainsonine”. International Immunopharmacology 3 (10-11): 1537–47. doi:10.1016/S1567-5769(03)00186-3. PMID 12946451.
- ^ Klein JL, Roberts JD, George MD, Kurtzberg J, Breton P, Chermann JC, Olden K (1999). “Swainsonine protects both murine and human haematopoietic systems from chemotherapeutic toxicity”. Br. J. Cancer 80 (1-2): 87–95. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6690326. PMID 10389983.
- ^ Pritchard DH, Huxtable CR, Dorling PR (1990). “Swainsonine toxicosis suppresses appetite and retards growth in weanling rats”. Research in Veterinary Science 48 (2): 228–30. PMID 2110378.
関連項目
外部リンク
- Swainsonine at Logan Natural Products
- Swainsonine from Tocris Bioscience
スワインソニンと同じ種類の言葉
- スワインソニンのページへのリンク