CGP‐7930
CGP-7930
出典: フリー百科事典『ウィキペディア(Wikipedia)』 (2025/09/09 23:36 UTC 版)
 |
|
| 臨床データ | |
|---|---|
| 識別子 | |
|
|
| CAS登録番号 | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox ダッシュボード (EPA) |
|
| 化学的および物理的データ | |
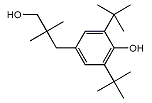
| 化学式 | C19H32O2 |
| 分子量 | 292.46 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
|
SMILES
|
|
|
|
|
  (what is this?) (verify) (what is this?) (verify) |
|
CGP-7930は、文献で初めて報告されたGABAB受容体の陽性アロステリック調節因子である[1][2][3][4]。CGP7930は、GABAA受容体の陽性アロステリック調節因子であり、カリウムチャネル遮断薬でもある[5]。
CGP7930はノバルティスによって開発され、科学研究に広く使用されてきた。動物実験では抗不安作用を持ち[6][7]、バクロフェンやGHBなどのGABABアゴニストとの相乗効果を持ち[8][9]、アルコール飲料やコカインの自己投与を減少させる[10][11]。
CNSレビュー:[12]
合成
化学合成は以下の通りである[13]:出発物質[14]:第一段階の生成物[15][16]:

2,6-ジ-tert-ブチルフェノールをホルムアルデヒド、塩基及びメタノールと反応させると、[87-97-8] (2)が得られる。イソブタールデヒドを用いた塩基触媒反応によりCGP-13501(3)が得られる。アルデヒドのヒドリド還元により、第一級アルコールが生成する。

Krysin(ロシア)によれば、2,6-ジ-tert-ブチルフェノールはオートクレーブ内で苛性ソーダを用いてネオペンチルグリコールと反応させる。一段階反応であるにもかかわらず、収率はわずか15%と報告されている[17]。
出典
- ^ “Positive allosteric modulation of native and recombinant gamma-aminobutyric acid(B) receptors by 2,6-Di-tert-butyl-4-(3-hydroxy-2,2-dimethyl-propyl)-phenol (CGP7930) and its aldehyde analog CGP13501”. Molecular Pharmacology 60 (5): 963–71. (November 2001). PMID 11641424.
- ^ “The heptahelical domain of GABA(B2) is activated directly by CGP7930, a positive allosteric modulator of the GABA(B) receptor”. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 279 (28): 29085–91. (July 2004). doi:10.1074/jbc.M400930200. PMC 2557059. PMID 15126507.
- ^ “Differential modulation by the GABAB receptor allosteric potentiator 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-(3-hydroxy-2,2-dimethylpropyl)-phenol (CGP7930) of synaptic transmission in the rat hippocampal CA1 area”. The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 317 (3): 1170–7. (June 2006). doi:10.1124/jpet.105.099176. PMID 16507713.
- ^ “CGP7930: a positive allosteric modulator of the GABAB receptor”. CNS Drug Reviews 13 (3): 308–16. doi:10.1111/j.1527-3458.2007.00021.x. PMC 6494120. PMID 17894647.
- ^ “CGP7930 - An allosteric modulator of GABABRs, GABAARs and inwardly-rectifying potassium channels”. Neuropharmacology 109644. (July 2023). doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2023.109644. PMID 37422181.
- ^ “Effects of GABAB receptor ligands in animal tests of depression and anxiety”. Pharmacological Reports 59 (6): 645–55. PMID 18195453.
- ^ “Evaluation of the anxiolytic-like profile of the GABAB receptor positive modulator CGP7930 in rodents”. Neuropharmacology 54 (5): 854–62. (April 2008). doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2008.01.004. PMID 18328507.
- ^ “In vivo effectiveness of CGP7930, a positive allosteric modulator of the GABAB receptor”. European Journal of Pharmacology 504 (3): 213–6. (November 2004). doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2004.10.008. PMID 15541424.
- ^ “The CGP7930 analogue 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-(3-hydroxy-2-spiropentylpropyl)-phenol (BSPP) potentiates baclofen action at GABA(B) autoreceptors”. Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology & Physiology 35 (9): 1113–5. (September 2008). doi:10.1111/j.1440-1681.2008.04948.x. PMID 18430050.
- ^ “The GABA(B) receptor allosteric modulator CGP7930, like baclofen, reduces operant self-administration of ethanol in alcohol-preferring rats”. Neuropharmacology 50 (5): 632–9. (April 2006). doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2005.11.011. PMID 16406445.
- ^ “Effects of GABA(B) receptor antagonist, agonists and allosteric positive modulator on the cocaine-induced self-administration and drug discrimination”. European Journal of Pharmacology 574 (2-3): 148–57. (November 2007). doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.07.048. PMID 17698060.
- ^ Ong, J., Kerr, D. I. B. (September 2005). "Clinical Potential of GABA B Receptor Modulators". CNS Drug Reviews. 11 (3): 317–334. doi:10.1111/j.1527-3458.2005.tb00049.x.
- ^ Kerr, David I. B.; Khalafy, Jabbar; Ong, Jennifer; Perkins, Michael V.; Prager, Rolf H.; Puspawati, Ni Made; Rimaz, Mehdi (2006). "Synthesis and Biological Activity of Allosteric Modulators of GABABReceptors, Part 2. 3-(2,6-Bis-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propanols". Australian Journal of Chemistry. 59 (7): 457. doi:10.1071/CH06164.
- ^ Richard Henry Kline, EP0027426 (1983 to The Goodyear Tire & Rubber Company).
- ^ “Reactions of Hindered Phenols. I. Reactions of 4,4’-Dihydroxy-3,5,3’,5’-tetra-tert-butyl Diphenylmethane *”. The Journal of Organic Chemistry 22 (11): 1435–1438. (November 1957). doi:10.1021/jo01362a033.
- ^ “Single crystal X-ray structure of 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-(3-(4-chlorophenyl)-4-methyl-4,5-dihydroisoxazol-5-yl)phenol 1,4-dioxane hemisolvate”. Journal of Structural Chemistry 54 (1): 217–222. (February 2013). doi:10.1134/S0022476613010368.
- ^ Krysin, A. P.; Pustovskikh, I. I.; Koptyug, V. A. (2010). "Synthesis of 4-(ω-hydroxyalkyl)-2,6-di-tert-butylphenols and the properties of related sulfides". Russian Journal of General Chemistry. 80 (10): 2001–2006. doi:10.1134/S1070363210100208.
- CGP‐7930のページへのリンク