Abstract
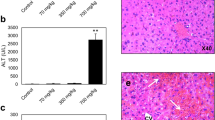
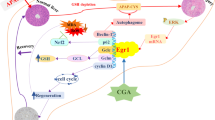
Since xenobiotics enter the organism via the liver, hepatocytes must cope with numerous perturbations, including modifications of proteins leading to endoplasmic reticulum stress (ER-stress). This triggers a signaling pathway termed unfolded protein response (UPR) that aims to restore homeostasis or to eliminate disturbed hepatocytes by apoptosis. In the present study, we used the well-established CCl4 hepatotoxicity model in mice to address the questions whether CCl4 induces ER-stress and, if so, whether the well-known ER-stress effector CHOP is responsible for CCl4-induced apoptosis. For this purpose, we treated mice with a high dose of CCl4 injected i.p. and followed gene expression profile over time using Affymetrix gene array analysis. This time resolved gene expression analysis allowed the identification of gene clusters with overrepresented binding sites for the three most important ER-stress induced transcription factors, CHOP, XBP1 and ATF4. Such result was confirmed by the demonstration of CCl4-induced XBP1 splicing, upregulation of CHOP at mRNA and protein levels, and translocation of CHOP to the nucleus. Two observations indicated that CHOP may be responsible for CCl4-induced cell death: (1) Nuclear translocation of CHOP was exclusively observed in the pericentral fraction of hepatocytes that deteriorate in response to CCl4 and (2) CHOP-regulated genes with previously reported pro-apoptotic function such as GADD34, TRB3 and ERO1L were induced in the pericentral zone as well. Therefore, we compared CCl4 induced hepatotoxicity in CHOP knockout versus wild-type mice. Surprisingly, genetic depletion of CHOP did not afford protection against CCl4-induced damage as evidenced by serum GOT and GPT as well as quantification of dead tissue areas. The negative result was obtained at several time points (8, 24 and 72 h) and different CCl4 doses (1.6 and 0.132 g/kg). Overall, our results demonstrate that all branches of the UPR are activated in mouse liver upon CCl4 treatment. However, CHOP does not play a critical role in CCl4-induced cell death and cannot be considered as a biomarker strictly linked to hepatotoxicity. The role of alternative UPR effectors such as XBP1 remains to be investigated.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ER:
-
Endoplasmic reticulum
- APAP:
-
n-Acetyl-p-aminophenol
- CCl4 :
-
Carbon tetrachloride
- I.P.:
-
Intraperitoneal
References
Bansal MB, Kovalovich K, Gupta R, Li W, Agarwal A, Radbill B, Alvarez CE, Safadi R, Fiel MI, Friedman SL, Taub RA (2005) Interleukin-6 protects hepatocytes from CCl4-mediated necrosis and apoptosis in mice by reducing MMP-2 expression. J Hepatol 42(4):548–556
Benedetti G, Ramaiahgaris S, Herpers B, van de Water B, Price LS, de Graauw M (2013) A screen for apoptotic synergism between clinical relevant nephrotoxicant and the cytokine TNF-alpha. Toxicol In Vitro 27(8):2264–2272
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y (1995) Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc 57(1):289–300
Bezdek JC, Hathaway RJ (1992) Numerical convergence and interpretation of the fuzzy c-shells clustering algorithm. IEEE Trans Neural Netw (a publication of the IEEE Neural Networks Council) 3(5):787–793
Bolstad BM (2004) Low level analysis of high-density oligonucleotide array data: background, normalization and summarization. University of California, Berkeley
Cribb AE, Peyrou M, Muruganandan S, Schneider L (2005) The endoplasmic reticulum in xenobiotic toxicity. Drug Metab Rev 37(3):405–442
Dai M, Wang P, Boyd AD, Kostov G, Athey B, Jones EG, Bunney WE, Myers RM, Speed TP, Akil H, Watson SJ, Meng F (2005) Evolving gene/transcript definitions significantly alter the interpretation of GeneChip data. Nucleic Acids Res 33(20):e175
Elkon R, Linhart C, Sharan R, Shamir R, Shiloh Y (2003) Genome-wide in silico identification of transcriptional regulators controlling the cell cycle in human cells. Genome Res 13(5):773–780
Gentleman RC, Carey VJ, Bates DM, Bolstad B, Dettling M, Dudoit S, Ellis B, Gautier L, Ge Y, Gentry J, Hornik K, Hothorn T, Huber W, Iacus S, Irizarry R, Leisch F, Li C, Maechler M, Rossini AJ, Sawitzki G, Smith C, Smyth G, Tierney L, Yang JY, Zhang J (2004) Bioconductor: open software development for computational biology and bioinformatics. Genome Biol 5(10):R80
Godoy P, Hengstler JG, Ilkavets I, Meyer C, Bachmann A, Muller A, Tuschl G, Mueller SO, Dooley S (2009) Extracellular matrix modulates sensitivity of hepatocytes to fibroblastoid dedifferentiation and transforming growth factor beta-induced apoptosis. Hepatology (Baltimore, MD) 49(6):2031–2043
Godoy P, Hewitt NJ, Albrecht U, Andersen ME, Ansari N, Bhattacharya S, Bode JG, Bolleyn J, Borner C, Bottger J, Braeuning A, Budinsky RA, Burkhardt B, Cameron NR, Camussi G, Cho CS, Choi YJ, Craig Rowlands J, Dahmen U, Damm G, Dirsch O, Donato MT, Dong J, Dooley S, Drasdo D, Eakins R, Ferreira KS, Fonsato V, Fraczek J, Gebhardt R, Gibson A, Glanemann M, Goldring CE, Gomez-Lechon MJ, Groothuis GM, Gustavsson L, Guyot C, Hallifax D, Hammad S, Hayward A, Haussinger D, Hellerbrand C, Hewitt P, Hoehme S, Holzhutter HG, Houston JB, Hrach J, Ito K, Jaeschke H, Keitel V, Kelm JM, Kevin Park B, Kordes C, Kullak-Ublick GA, Lecluyse EL, Lu P, Luebke-Wheeler J, Lutz A, Maltman DJ, Matz-Soja M, McMullen P, Merfort I, Messner S, Meyer C, Mwinyi J, Naisbitt DJ, Nussler AK, Olinga P, Pampaloni F, Pi J, Pluta L, Przyborski SA, Ramachandran A, Rogiers V, Rowe C, Schelcher C, Schmich K, Schwarz M, Singh B, Stelzer EH, Stieger B, Stober R, Sugiyama Y, Tetta C, Thasler WE, Vanhaecke T, Vinken M, Weiss TS, Widera A, Woods CG, Xu JJ, Yarborough KM, Hengstler JG (2013) Recent advances in 2D and 3D in vitro systems using primary hepatocytes, alternative hepatocyte sources and non-parenchymal liver cells and their use in investigating mechanisms of hepatotoxicity, cell signaling and ADME. Arch Toxicol 87(8):1315–1530
Gunawan BK, Liu ZX, Han D, Hanawa N, Gaarde WA, Kaplowitz N (2006) c-Jun N-terminal kinase plays a major role in murine acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. Gastroenterology 131(1):165–178
Han J, Back SH, Hur J, Lin YH, Gildersleeve R, Shan J, Yuan CL, Krokowski D, Wang S, Hatzoglou M, Kilberg MS, Sartor MA, Kaufman RJ (2013) ER-stress-induced transcriptional regulation increases protein synthesis leading to cell death. Nat Cell Biol 15(5):481–490
Hetz C (2012) The unfolded protein response: controlling cell fate decisions under ER stress and beyond. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 13(2):89–102
Hetz C, Glimcher LH (2009) Fine-tuning of the unfolded protein response: assembling the IRE1alpha interactome. Mol Cell 35(5):551–561
Hetz C, Martinon F, Rodriguez D, Glimcher LH (2011) The unfolded protein response: integrating stress signals through the stress sensor IRE1alpha. Physiol Rev 91(4):1219–1243
Hoehme S, Brulport M, Bauer A, Bedawy E, Schormann W, Hermes M, Puppe V, Gebhardt R, Zellmer S, Schwarz M, Bockamp E, Timmel T, Hengstler JG, Drasdo D (2010) Prediction and validation of cell alignment along microvessels as order principle to restore tissue architecture in liver regeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(23):10371–10376
Horiguchi N, Lafdil F, Miller AM, Park O, Wang H, Rajesh M, Mukhopadhyay P, Fu XY, Pacher P, Gao B (2010) Dissociation between liver inflammation and hepatocellular damage induced by carbon tetrachloride in myeloid cell-specific signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 gene knockout mice. Hepatology (Baltimore, MD) 51(5):1724–1734
Jaeschke H, Williams CD, Ramachandran A, Bajt ML (2011) Acetaminophen hepatotoxicity and repair: the role of sterile inflammation and innate immunity. Liver Int 32(1):8–20
Jaeschke H, Williams CD, McGill MR, Xie Y, Ramachandran A (2013) Models of drug-induced liver injury for evaluation of phytotherapeutics and other natural products. Food Chem Toxicol 55:279–289
Jang EH, Park CS, Kang JH (2011) Bupropion, an atypical antidepressant, induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and caspase-dependent cytotoxicity in SH-SY5Y cells. Toxicology 285(1–2):1–7
Ji C, Mehrian-Shai R, Chan C, Hsu YH, Kaplowitz N (2005) Role of CHOP in hepatic apoptosis in the murine model of intragastric ethanol feeding. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 29(8):1496–1503
Ji YL, Wang H, Zhao XF, Wang Q, Zhang C, Zhang Y, Zhao M, Chen YH, Meng XH, Xu DX (2011) Crosstalk between endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondrial pathway mediates cadmium-induced germ cell apoptosis in testes. Toxicol Sci 124(2):446–459
Lafleur MA, Stevens JL, Lawrence JW (2013) Xenobiotic perturbation of ER stress and the unfolded protein response. Toxicol Pathol 41(2):235–262
Laurent V, Fraix A, Montier T, Cammas-Marion S, Ribault C, Benvegnu T, Jaffres PA, Loyer P (2010) Highly efficient gene transfer into hepatocyte-like HepaRG cells: new means for drug metabolism and toxicity studies. Biotechnol J 5(3):314–320
Li G, Mongillo M, Chin KT, Harding H, Ron D, Marks AR, Tabas I (2009) Role of ERO1-alpha-mediated stimulation of inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate receptor activity in endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis. J Cell Biol 186(6):783–792
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods (San Diego, CA) 25(4):402–408
Ma Y, Hendershot LM (2003) Delineation of a negative feedback regulatory loop that controls protein translation during endoplasmic reticulum stress. J Biol Chem 278(37):34864–34873
Malhi H, Kaufman RJ (2011) Endoplasmic reticulum stress in liver disease. J Hepatol 54(4):795–809
Mao C, Dong D, Little E, Luo S, Lee AS (2004) Transgenic mouse model for monitoring endoplasmic reticulum stress in vivo. Nat Med 10(10):1013–1014 (author reply 1014)
Marciniak SJ, Yun CY, Oyadomari S, Novoa I, Zhang Y, Jungreis R, Nagata K, Harding HP, Ron D (2004) CHOP induces death by promoting protein synthesis and oxidation in the stressed endoplasmic reticulum. Genes Dev 18(24):3066–3077
McCullough KD, Martindale JL, Klotz LO, Aw TY, Holbrook NJ (2001) Gadd153 sensitizes cells to endoplasmic reticulum stress by down-regulating Bcl2 and perturbing the cellular redox state. Mol Cell Biol 21(4):1249–1259
Meng Z, Wang Y, Wang L, Jin W, Liu N, Pan H, Liu L, Wagman L, Forman BM, Huang W (2010) FXR regulates liver repair after CCl4-induced toxic injury. Mol Endocrinol (Baltimore, MD) 24(5):886–897
Ohoka N, Yoshii S, Hattori T, Onozaki K, Hayashi H (2005) TRB3, a novel ER stress-inducible gene, is induced via ATF4-CHOP pathway and is involved in cell death. EMBO J 24(6):1243–1255
Oyadomari S, Mori M (2004) Roles of CHOP/GADD153 in endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Death Differ 11(4):381–389
Poli G, Cottalasso D, Pronzato MA, Chiarpotto E, Biasi F, Corongiu FP, Marinari UM, Nanni G, Dianzani MU (1990) Lipid peroxidation and covalent binding in the early functional impairment of liver Golgi apparatus by carbon tetrachloride. Cell Biochem Funct 8(1):1–10
Puthalakath H, O’Reilly LA, Gunn P, Lee L, Kelly PN, Huntington ND, Hughes PD, Michalak EM, McKimm-Breschkin J, Motoyama N, Gotoh T, Akira S, Bouillet P, Strasser A (2007) ER stress triggers apoptosis by activating BH3-only protein Bim. Cell 129(7):1337–1349
Ron D, Walter P (2007) Signal integration in the endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8(7):519–529
Sekine S, Ogawa R, Kanai Y (2011) Hepatomas with activating Ctnnb1 mutations in ‘Ctnnb1-deficient’ livers: a tricky aspect of a conditional knockout mouse model. Carcinogenesis 32(4):622–628
Shi J, Aisaki K, Ikawa Y, Wake K (1998) Evidence of hepatocyte apoptosis in rat liver after the administration of carbon tetrachloride. Am J Pathol 153(2):515–525
Silva RM, Ries V, Oo TF, Yarygina O, Jackson-Lewis V, Ryu EJ, Lu PD, Marciniak SJ, Ron D, Przedborski S, Kholodilov N, Greene LA, Burke RE (2005) CHOP/GADD153 is a mediator of apoptotic death in substantia nigra dopamine neurons in an in vivo neurotoxin model of Parkinsonism. J Neurochem 95(4):974–986
Smyth GK (2005) Limma: linear models for microarray data. In: Gentleman R, Carey V, Dudoit S, Irizarry R, Huber W (eds) Bioinformatics and computational biology solutions using r and bioconductor. Springer, New York, pp 397–420
Song B, Scheuner D, Ron D, Pennathur S, Kaufman RJ (2008) Chop deletion reduces oxidative stress, improves beta cell function, and promotes cell survival in multiple mouse models of diabetes. J Clin Investig 118(10):3378–3389
Tabas I, Ron D (2011) Integrating the mechanisms of apoptosis induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress. Nat Cell Biol 13(3):184–190
Thorp E, Li G, Seimon TA, Kuriakose G, Ron D, Tabas I (2009) Reduced apoptosis and plaque necrosis in advanced atherosclerotic lesions of Apoe-/- and Ldlr-/- mice lacking CHOP. Cell Metab 9(5):474–481
Ulitsky I, Maron-Katz A, Shavit S, Sagir D, Linhart C, Elkon R, Tanay A, Sharan R, Shiloh Y, Shamir R (2010) Expander: from expression microarrays to networks and functions. Nat Protoc 5(2):303–322
Uzi D, Barda L, Scaiewicz V, Mills M, Mueller T, Gonzalez-Rodriguez A, Valverde AM, Iwawaki T, Nahmias Y, Xavier R, Chung RT, Tirosh B, Shibolet O (2013) CHOP is a critical regulator of acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity. J Hepatol 59(3):495–503
Weber LW, Boll M, Stampfl A (2003) Hepatotoxicity and mechanism of action of haloalkanes: carbon tetrachloride as a toxicological model. Crit Rev Toxicol 33(2):105–136
Zellmer S, Schmidt-Heck W, Godoy P, Weng H, Meyer C, Lehmann T, Sparna T, Schormann W, Hammad S, Kreutz C, Timmer J, von Weizsacker F, Thurmann PA, Merfort I, Guthke R, Dooley S, Hengstler JG, Gebhardt R (2010) Transcription factors ETF, E2F, and SP-1 are involved in cytokine-independent proliferation of murine hepatocytes. Hepatology (Baltimore, MD) 52(6):2127–2136
Zinszner H, Kuroda M, Wang X, Batchvarova N, Lightfoot RT, Remotti H, Stevens JL, Ron D (1998) CHOP is implicated in programmed cell death in response to impaired function of the endoplasmic reticulum. Genes Dev 12(7):982–995
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the SEURAT-1 projects NOTOX (EU-project FP7-Health Grant Agreement No. 267038) and DETECTIVE (EU-project FP7-Health Grant Agreement No. 266838) and the BMBF (German Federal Ministry of Education and Research) project Virtual Liver (0313854). We acknowledge support from FONDECYT (1140549), Millennium Institute (P09-015-F), Ring Initiative (ACT1109) (to C.H.), and FONDECYT (3130351 to D.B.M.).
Conflict of interest
None of the authors have a conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Campos, G., Schmidt-Heck, W., Ghallab, A. et al. The transcription factor CHOP, a central component of the transcriptional regulatory network induced upon CCl4 intoxication in mouse liver, is not a critical mediator of hepatotoxicity. Arch Toxicol 88, 1267–1280 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-014-1240-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-014-1240-8