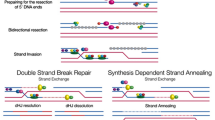
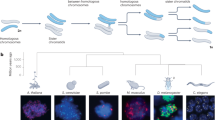
Abstract
In archaea, sexual communication during mating includes transferring information (segments of DNA) to a second cell, apparently promoting DNA repair in the recipient. This process involves recombination between homologous DNA molecules from the two cells. Meiosis is a general capability of eukaryotes, and accumulating evidence indicates that the common ancestor of all eukaryotes was capable of meiosis. A central feature of meiosis is the recombination of homologous DNA molecules, ordinarily from two individuals (parents). Here, we present evidence that archaeal mating was the likely ancestral precursor to eukaryotic meiotic sex. In both archaea and eukaryotic microorganisms, the sexual cycle is induced by stresses that can cause DNA damage. Meiosis appears to have evolved in complexity from the simpler archaeal ancestral recombinational process. This evolution in complexity was likely part of a general protective response to DNA damaging reactive oxygen species produced by the proto-mitochondria during the prokaryotic to eukaryotic transition.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajon M, Fröls S, van Wolferen M, Stoecker K, Teichmann D, Driessen AJ, Grogan DW, Albers SV, Schleper C (2011) UV-inducible DNA exchange in hyperthermophilic archaea mediated by type IV pili. Mol Microbiol 82(4):807–817
Akopyants NS, Kimblin N, Secundino N, Patrick R, Peters N, Lawyer P, Dobson DE, Beverley SM, Sacks DL (2009) Demonstration of genetic exchange during cyclical development of Leishmania in the sand fly vector. Science 324(5924):265–268
Allers T (2011) Swapping genes to survive—a new role for archaeal type IV pili. Mol Microbiol 82(4):789–791
Andersson SG, Zomorodipour A, Andersson JO, Sicheritz-Pontén T, Alsmark UC, Podowski RM, Näslund AK, Eriksson AS, Winkler HH, Kurland CG (1998) The genome sequence of Rickettsia prowazekii and the origin of mitochondria. Nature 396(6707):133–140
Bernstein H, Bernstein C (2010) Evolutionary origin of recombination during meiosis. Bioscience 60(7):498–505
Bernstein C, Bernstein H (2013) Evolutionary origin and adaptive function of meiosis. In: Bernstein C, Bernstein H (eds) Meiosis. InTech, Rijeka, Croatia, pp 41–45
Bernstein C, Johns V (1989) Sexual reproduction as a response to H2O2 damage in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. J Bacteriol 171(4):1893–1897
Bernstein H, Byerly HC, Hopf FA, Michod RE (1984) Origin of sex. J Theor Biol 110(3):323–351
Boubriak I, Ng WL, DasSarma P, DasSarma S, Crowley DJ, McCready SJ (2008) Transcriptional responses to biologically relevant doses of UV-B radiation in the model archaeon, Halobacterium sp. NRC-1. Saline Syst 4:13
Butterfield NJ (2000) Bangiomorpha pubescens n. gen., n.sp.: implications for the evolution of sex, multicellularity, and the Mesoproterozoic/Neoproterozoic radiation of eukaryotes. Paleobiology 26(3):386–404
Cotton JA, McInerney JO (2010) Eukaryotic genes of archaebacterial origin are more important than the more numerous eubacterial genes, irrespective of function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(40):17252–17255
Cox CJ, Foster PG, Hirt RP, Harris SR, Embley TM (2008) The archaebacterial origin of eukaryotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(51):20356–20361
Dacks J, Roger AJ (1999) The first sexual lineage and the relevance of facultative sex. J Mol Evol 48(6):779–783
Davey J (1998) Fusion of a fission yeast. Yeast 14(16):1529–1566
Davidov Y, Huchon D, Koval SF, Jurkevitch E (2006) A new alpha-proteobacterial clade of Bdellovibrio-like predators: implications for the mitochondrial endosymbiotic theory. Environ Microbiol 8(12):2179–2188
Demanèche S, Kay E, Gourbière F, Simonet P (2001) Natural transformation of Pseudomonas fluorescens and Agrobacterium tumefaciens in soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 67(6):2617–2621
Elliott AM, Hayes RE (1953) Mating types in tetrahymena. Biol Bull 105:269–284
Fröls S, Ajon M, Wagner M, Teichmann D, Zolghadr B, Folea M, Boekema EJ, Driessen AJ, Schleper C, Albers SV (2008) UV-inducible cellular aggregation of the hyperthermophilic archaeon Sulfolobus solfataricus is meciated by pili formation. Mol Microbiol 70(4):938–952
Fröls S, White MF, Schleper C (2009) Reactions to UV damage in the model archaeon Sulfolobus solfataricus. Biochem Soc Trans 37(Pt 1):36–41
Gabaldón T, Huynen MA (2003) Reconstruction of the proto-mitochondrial metabolism. Science 301(5633):609
Gaudin M, Gauliard E, Schouten S, Houel-Renault L, Lenormand P, Marguet E, Forterre P (2013) Hyperthermophilic archaea produce membrane vesicles that can transfer DNA. Environ Microbiol Rep 5(1):109–116
Gray MW, Burger G, Lang BF (1999) Mitochondrial Evolution. Sci 283:1476–1481
Gray TA, Krywy JA, Harold J, Palumbo MJ, Derbyshire KM (2013) Distributive conjugal transfer in mycobacteria generates progeny with meiotic-like genome-wide mosaicism, allowing mapping of a mating identity locus. PLoS Biol 11(7):e1001602. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1001602
Grogan DW (1996) Exchange of genetic markers at extremely high temperatures in the archaeon Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. J Bacteriol 178(11):3207–3211
Guerrero R, Pedros-Alio C, Esteve I, Mas J, Chase D, Margulis L (1986) Predatory prokaryotes: predation and primary consumption evolved in bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83(7):2138–2142
Halary S, Malik S-B, Lildhar L, Slarnovits CH, Hijri M, Corradi N (2011) Conserved meiotic machinery in Glomus spp., a putatively ancient asexual fungal lineage. Genome Biol Evol 3:950–958
Hampl V, Hug L, Leigh JW, Dacks JB, Lang BF, Simpson AG, Roger AJ (2009) Phylogenomic analyses support the monophyly of excavata and resolve relationships among eukaryotic “supergroups”. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(10):3859–3864
Herskowitz I (1988) Life cycle of the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiol Rev 52(4):536–553
Javaux EJ, Knoll AH, Walter MR (2001) Morphological and ecological complexity in early eukaryote ecosystems. Nature 412:66–69
Johnson A (2003) The biology of mating in Candida albicans. Nat Rev Microbiol 1(2):106–116
Kirk DL, Kirk MM (1986) Heat shock elicits production of sexual inducer in Volvox. Science 231(4733):51–54
Lahr DJ, Parfrey LW, Mitchell EA, Katz LA, Lara E (2011) The chastity of amoebae: re-evaluating evidence for sex in amoeboid organisms. Proc Biol Sci 278(1715):2081–2090
Malik SB, Pightling AW, Stefaniak LM, Schurko AM, Logsdon JM Jr (2008) An expanded inventory of conserved meiotic genes provides evidence for sex in Trichomonas vaginalis. PLoS ONE 3(8):e2879. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0002879
Mans BJ, Anantharaman V, Aravind L, Koonin EV (2004) Comparative genomics, evolution and origins of the nuclear envelope and nuclear pore complex. Cell Cycle 3(12):1612–1637
Martin W (2005) Archaebacteria (Archaea) and the origin of the eukaryotic nucleus. Curr Opin Microbiol 8(6):630–637
McCready S, Müller JA, Boubriak I, Berquist BR, Ng WL, DasSarma S (2005) UV irradiation induces homologous recombination genes in the model archaeon, Halobacterium sp. NRC-1. Saline Syst 1:3
Millard JT (1996) DNA modifying agents as tools for studying chromatin structure. Biochimie 78(10):803–816
Naor A, Gophna U (2013) Cell fusion and hybrids in Archaea: prospects for genome shuffling and accelerated strain development for biotechnology. Bioengineered 4(3):126–129
Nedelcu AM, Michod RE (2003) Sex as a response to oxidative stress: the effect of antioxidants on sexual induction in a facultatively sexual lineage. Proc Biol Sci 7(270 Suppl 2):136–139
Nedelcu AM, Marcu O, Michod RE (2004) Sex as a response to oxidative stress: a twofold increase in cellular reactive oxygen species activates sex genes. Proc Biol Sci 271(1548):1591–1596
O’Connor M, Wopat A, Hanson RS (1977) Genetic transformation in Methylobacterium organophilum. J Gen Microbiol 98(1):265–272
Papke RT, Koenig JE, Rodríguez-Valera F, Doolittle WF (2004) Frequent recombination in a saltern population of Halorubrum. Science 306(5703):1928–1929
Peacock L, Bailey M, Carrington M, Gibson W (2014) Meiosis and haploid gametes in the pathogen Trypanosoma brucei. Curr Biol 24(2):181–186
Quaiser A, Constantinesco F, White MF, Forterre P, Elie C (2008) The Mre11 protein interacts with both Rad50 and the HerA bipolar helicase and is recruited to DNA following gamma irradiation in the archaeon Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. BMC Mol Biol 9:25. doi:10.1186/1471-2199-9-25
Raina JL, Modi VV (1972) Deoxyribonucleate binding and transformation in Rhizobium jpaonicum. J Bacteriol 111(2):356–360
Ramesh MA, Malik SB, Logsdon JM Jr (2005) A phylogenomic inventory of meiotic genes; evidence for sex in Giardia and an early eukaryotic origin of meiosis. Curr Biol 15(2):185–191
Reeves RJ, Jackson RM (1974) Stimulation of sexual reproduction in Phytophthora by damage. J Gen Microbiol 84:303–310
Reilly MS, Grogan DW (2002) Biological effects of DNA damage in the hyperthermophilic archaeon Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. FEMS Microbiol Lett 208(1):29–34
Rosenshine I, Tchelet R, Mevarech M (1989) The mechanism of DNA transfer in the mating system of an archaebacterium. Science 245(4924):1387–1389
Rzechorzek NJ, Blackwood JK, Bray SM, Maman JD, Pellegrini L, Robinson NP (2014) Structure of the hexameric HerA ATPase reveals a mechanism of translocation-coupled DNA-end processing in archaea. Nat Commun 5:5506. doi:10.1038/ncomms6506
Sager R, Granick S (1954) Nutritional control of sexuality in Chlamydomonas reinhardi. J Gen Physiol 37(6):729–742
Seitz EM, Brockman JP, Sandler SJ, Clark AJ, Kowalczykowski SC (1998) RadA protein is an archaeal RecA protein homolog that catalyzes DNA strand exchange. Genes Dev 12(9):1248–1253
She Q, Singh RK, Confalonieri F, Zivanovic Y, Allard G, Awayez MJ, Chan-Weiher CC, Clausen IG, Curtis BA, De Moors A, Erauso G, Fletcher C, Gordon PM, Heikamp-de Jong I, Jeffries AC, Kozera CJ, Medina N, Peng X, Thi-Ngoc HP, Redder P, Schenk ME, Theriault C, Tolstrup N, Charlebois RL, Doolittle WF, Duguet M, Gaasterland T, Garrett RA, Ragan MA, Sensen CW, Van der Oost J (2001) The complete genome of the crenarchaeon Sulfolobus solfataricus P2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98(14):7835–7840
Slupphaug G, Kavli B, Krokan HE (2003) The interacting pathways for prevention and repair of oxidative DNA damage. Mutat Res 531(1–2):231–251
Speijer D (2015) Birth of the eukaryotes by a set of reactive innovations: new insights force us to relinquish gradual models. BioEssays 37(12):1268–1276
Speijer D, Lukeš J, Eliáš M (2015) Sex is a ubiquitous, ancient, and inherent attribute of eukaryotic life. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112(29):8827–8834
Thiergart T, Landan G, Schenk M, Dagan T, Martin WF (2012) An evolutionary network of genes present in the eukaryote common ancestor polls genomes on eukaryotic and mitochondrial origin. Genome Biol Evol 4(4):466–485
van Wolferen M, Ajon M, Driessen AJ, Albers SV (2013) Molecular analysis of the UV-inducible pili operon from Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. Microbiologyopen 2(6):928–937. doi:10.1002/mbo3.128
van Wolferen M, Ma X, Albers SV (2015) DNA Processing proteins involved in the UV induced stress response of Sulfolobales. J Bacteriol 197(18):2941–2951
van Wolferen M, Wagner A, van der Does C, Albers SV (2016) The archaeal Ced system imports DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113(9):2496–2501
White MF (2011) Homologous recombination in the archaea: the means justify the ends. Biochem Soc Trans. 39(1):15–19. doi:10.1042/BST0390015. Review. PMID: 21265740
Wood ER, Ghané F, Grogan DW (1997) Genetic responses of the thermophilic archaeon Sulfolobus acidocaldarius to short-wavelength UV light. J Bacteriol 179(18):5693–5698
Wood V, Gwilliam R, Rajandream MA, Lyne M, Lyne R, Stewart A, Sgouros J, Peat N, Hayles J, Baker S, Basham D, Bowman S, Brooks K, Brown D, Brown S, Chillingworth T, Churcher C, Collins M, Connor R, Cronin A, Davis P, Feltwell T, Fraser A, Gentles S, Goble A, Hamlin N, Harris D, Hidalgo J, Hodgson G, Holroyd S, Hornsby T, Howarth S, Huckle EJ, Hunt S, Jagels K, James K, Jones L, Jones M, Leather S, McDonald S, McLean J, Mooney P, Moule S, Mungall K, Murphy L, Niblett D, Odell C, Oliver K, O’Neil S, Pearson D, Quail MA, Rabbinowitsch E, Rutherford K, Rutter S, Saunders D, Seeger K, Sharp S, Skelton J, Simmonds M, Squares R, Squares S, Stevens K, Taylor K, Taylor RG, Tivey A, Walsh S, Warren T, Whitehead S, Woodward J, Volckaert G, Aert R, Robben J, Grymonprez B, Weltjens I, Vanstreels E, Rieger M, Schäfer M, Müller-Auer S, Gabel C, Fuchs M, Düsterhöft A, Fritzc C, Holzer E, Moestl D, Hilbert H, Borzym K, Langer I, Beck A, Lehrach H, Reinhardt R, Pohl TM, Eger P, Zimmermann W, Wedler H, Wambutt R, Purnelle B, Goffeau A, Cadieu E, Dréano S, Gloux S, Lelaure V, Mottier S, Galibert F, Aves SJ, Xiang Z, Hunt C, Moore K, Hurst SM, Lucas M, Rochet M, Gaillardin C, Tallada VA, Garzon A, Thode G, Daga RR, Cruzado L, Jimenez J, Sánchez M, del Rey F, Benito J, Domínguez A, Revuelta JL, Moreno S, Armstrong J, Forsburg SL, Cerutti L, Lowe T, McCombie WR, Paulsen I, Potashkin J, Shpakovski GV, Ussery D, Barrell BG, Nurse P (2002) The genome sequence of Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Nature 415(6874):871–880
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer International Publishing AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Bernstein, H., Bernstein, C. (2017). Sexual Communication in Archaea, the Precursor to Eukaryotic Meiosis. In: Witzany, G. (eds) Biocommunication of Archaea. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-65536-9_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-65536-9_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-65535-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-65536-9
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)