Chestnut-headed tanager
| Chestnut-headed tanager | |
|---|---|

| |
| male | |

| |
| female | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Passeriformes |
| Family: | Thraupidae |
| Genus: | Thlypopsis |
| Species: | T. pyrrhocoma
|
| Binomial name | |
| Thlypopsis pyrrhocoma Burns, KJ, Unitt & Mason, NA, 2016
| |
| |
| Synonyms | |
|
Tachyphonus ruficeps | |
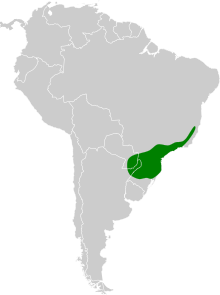
The chestnut-headed tanager (Thlypopsis pyrrhocoma) is a species of bird in the tanager family Thraupidae this is found in the Atlantic Forest of southeast Brazil, eastern Paraguay and far northeastern Argentina. It was formerly the only member of the genus Pyrrhocoma but is now placed in Thlypopsis.
Taxonomy[edit]
The chestnut-headed tanager was formally described in 1844 by the English naturalist Hugh Edwin Strickland under the binomial name Tachyphonus ruficeps.[2] The species was subsequently placed in the monotypic genus Pyrrhocoma by the German ornithologist Jean Cabanis.[3] A molecular phylogenetic study published in 2014 found that the chestnut-headed tanager was embedded in a clade containing members of the genus Thlypopsis.[4] The genera were therefore merged but as Thlypopsis already contained the rust-and-yellow tanager as Thlypopsis ruficeps d'Orbigny & Lafresnaye, 1837, a new specific epithet pyrrhocoma was coined for the chestnut-headed tanager, using the earlier generic name "to communicate past taxonomic connections".[5][6] The name comes from the Ancient Greek purrhokomēs meaning "red-haired".[7] The species is monotypic: no subspecies are recognised.[6]
References[edit]
- ^ BirdLife International (2016). "Thlypopsis pyrrhocoma". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T22722251A94757290. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22722251A94757290.en. Retrieved 11 November 2021.
- ^ Strickland, Hugh Edwin (1844). "Descriptions of several new or imperfectly-defined genera and species of birds". Annals and Magazine of Natural History. 13: 409–421 [419]. doi:10.1080/03745484409442625.
- ^ Cabanis, Jean; Heine, Ferdinand (1851). Museum Heineanum : Verzeichniss der ornithologischen Sammlung des Oberamtmann Ferdinand Heine, auf Gut St. Burchard vor Halberstadt (in German and Latin). Vol. 1. Halberstadt: R. Frantz. p. 138.
- ^ Burns, K.J.; Shultz, A.J.; Title, P.O.; Mason, N.A.; Barker, F.K.; Klicka, J.; Lanyon, S.M.; Lovette, I.J. (2014). "Phylogenetics and diversification of tanagers (Passeriformes: Thraupidae), the largest radiation of Neotropical songbirds". Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution. 75: 41–77. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2014.02.006. PMID 24583021.
- ^ Burns, K.J.; Unitt, P.; Mason, N.A. (2016). "A genus-level classification of the family Thraupidae (Class Aves: Order Passeriformes)". Zootaxa. 4088 (3): 329–354. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.4088.3.2. PMID 27394344.
- ^ a b Gill, Frank; Donsker, David; Rasmussen, Pamela, eds. (July 2020). "Tanagers and allies". IOC World Bird List Version 10.2. International Ornithologists' Union. Retrieved 18 October 2020.
- ^ Jobling, James A. (2010). The Helm Dictionary of Scientific Bird Names. London: Christopher Helm. p. 326. ISBN 978-1-4081-2501-4.

