Abstract
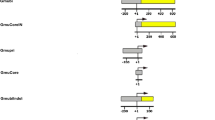
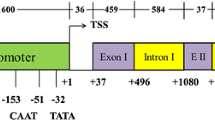
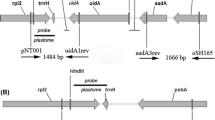
Glutamine synthetase (GS) catalyzes the synthesis of glutamine from glutamate and ammonia. In plants, it occurs as two major isoforms, a cytosolic form (GS1) and a nuclear encoded chloroplastic form. The focus of this paper is to determine the role of the 5′UTR of a GS1 gene. GS1 gene constructs with and without its 5′ and 3′ UTRs, driven by a constitutive promoter, were agroinfiltrated into tobacco leaves and the tissues were analyzed for both transgene transcript and protein accumulation. The constructs were also tested in an in vitro transcription/translation system and in Escherichia coli. Our results showed that while the 3′UTR functioned in the destabilization of the transcript, the 5′UTR acted as a translation enhancer in plant cells but not in the in vitro translation system. The 5′UTR of the GS1 gene when placed in front of a reporter gene (uidA), showed a 20-fold increase in the level of GUS expression in agroinfiltrated leaves when compared to the same gene construct without the 5′UTR. The 5′UTR-mediated translational enhancement is probably another step in the regulation of GS in plants. The presence of the GS1 5′UTR in front of the GS1 coding region allowed for its translation in E. coli suggesting the commonality of the translation initiation mechanism for this gene between plants and bacteria.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agalarov SC, Sogorin EA, Shirokikh NE, Spirin AS (2011) Insight into the structural organization of the omega leader of TMV RNA: the role of various regions of the sequence in the formation of a compact structure of the omega RNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 404:250–253
Beltran-Peña E, Aguilar R, Ortíz-Lopez A, Dinkova TD, Sánchez de Jiménez E (2002) Auxin stimulates S6 ribosomal protein phosphorylation in maize thereby affecting protein synthesis regulation. Physiol Plant 115:291–297
Bennett M, Cullimore J (1990) Expression of three plant glutamine synthetase cDNA in Escherichia coli. Formation of catalytically active isoenzymes, and complementation of a glnA mutant. Eur J Biochem 193:319–324
Bernard SM, Habash DZ (2009) The importance of cytosolic glutamine synthetase in nitrogen assimilation and recycling. New Phytol 182:608–620
Carvalho H, Sunkel C, Salema R, Cullimore JV (1997) Heteromeric assembly of the cytosolic glutamine synthetase polypeptides of Medicago truncatula: complementation of a glnA mutant with a plant domain-swapped enzyme. Plant Mol Biol 35:623–632
Dansako T, Kato K, Satoh J, Sekine M, Yoshida K, Shinmyo A (2003) 5′untranslated region of the HSP18.2 gene contributes to efficient translation in plant cells. J Biosci Bioeng 95:52–58
DasSarma S, Tisher E, Goodman HM (1986) Plant glutamine synthetase complements a glnA mutation in Escherichia coli. Science 232:1242–1244
Diaz C, Kusano M, Sulpice R, Araki M, Redestig H, Saito K, Stitt M, Shin R (2011) Determining novel functions of Arabidopsis 14-3-3 proteins in central metabolic processes BMC systems. Biol 5:192
Finneman J, Schjoerring JK (2000) Post-translational regulation of cytosolic glutamine synthetase genes by reversible phosphorylation and 14-3-3 protein interaction. Plant J 24:171–181
Gallie DR (2002) The 5′-leader of tobacco mosaic virus promotes translation through enhanced recruitment of eIF4F. Nucl Acids Res 30:3401–3411
Gray F, Tirabassi R, Meyers H, Wu G, McWeeney S, Hook L, Nelson JA (2010) A viral microRNA down-regulates multiple cell cycle genes through mRNA 5′UTRs. PLoS Pathog 6:e1000967
Hamilton TL, Stoneley Sprigs KA, Bushell M (2006) TOPs and their regulation. Biochem Soc Trans 34:12–16
Hulzink RJM, de Groot PFM, Croes AF, Quaedvlieg W, Twell D, Wullems GJ, van Herpen MMA (2002) The 5′-Untranslated region of the ntp303 gene strongly enhances translation during pollen tube growth, but not during pollen maturation. Plant Physiol 129:342–353
Jaeger JA, Turner DH, Zuker M (1989) Improved predictions of secondary structures for RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:7706–7710
Jefferson RA, Kavanagh TA, Bevan MW (1987) GUS fusions: β-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J 6:3901–3907
Jiang P, Ninfa AJ (2007) The Escherichia coli PII signal transduction protein controlling nitrogen assimilation acts as a sensor of adenylate energy charge in vitro. Biochemistry 37:12802–12810
Jiménez-López S, Mancera-Martínez E, Donayre-Torres A, Rangel C, Uribe L, March S, Jiménez-Sánchez G, Sánchez de Jiménez E (2011) Expression profile of maize (Zea mays L.) embryonic axes during germination: translational regulation of ribosomal protein mRNAs. Plant Cell Physiol 52:1719–1733
Kawaguchi R, Bailey-Serres J (2002) Regulation of translational initiation in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 5:460–465
Kawaguchi R, Bailey-Serres J (2005) mRNA sequence features that contribute to translational regulation in Arabidopsis. Nucl Acids Res 33:955–965
Komarova AV, Tchufistova LS, Supina EV, Boni IV (2002) Protein S1 counteracts the inhibitory effect of the extended Shine–Dalgarno sequence on translation. RNA 8:137–1147
Koscianska E, Kalantidis K, Wypijewski K, Sadowski J, Tabler M (2005) Analysis of RNA silencing in agroinfiltrated leaves of Nicotiana benthamiana and Nicotiana tabaccum. Plant Mol Biol 59:647–661
Kulkarni SD, Muralidharan B, Panda AC, Bakthavachalu B, Vindu A, Seshadri V (2011) Glucose-stimulated translation regulation of insulin by the 5′UTR-binding proteins. J Biol Chem 286:14146–14156
Kumada Y, Benson DR, Hillemann D, Hosted TJ, Rochefort DA, Thompson CJ, Wohlleben W, Tateno Y (1993) Evolution of the glutamine synthetase gene, one of the oldest existing and functioning genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:3009–3013
Leckie BM, Stewart CN (2011) Agroinfiltration as a technique for rapid assays for evaluating candidate insect resistance transgenes in plants. Plant Cell Rep 30:325–334
Lee K, Holland-Staley A, Cunninham PR (1996) Genetic analysis of the Shine–Dalgarno interaction: selection of alternative functional mRNA–rRNA combinations. RNA 2:1270–1285
Leigh JA, Dodsworth JA (2007) Nitrogen regulation in bacteria and Archaea. Annu Rev Microbiol 61:349–377
Lima L, Seabra A, Melo P, Cullimore J, Carvalho H (2006) Post-translational regulation of cytosolic glutamine synthetase of Medicago truncatula. J Exp Bot 57:2751–2767
Ma XM, Blenis J (2009) Molecular mechanisms of mTOR-mediated translational control. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10:307–318
Markham NR, Zuker M (2008) UNAFold: software for nucleic acid folding and hybridization. In: Keith JM (ed) Bioinformatics, vol II. Structure, function and applications, in methods in molecular biology, vol 453, pp 3–31. Humana Press, Totowa, NJ
McCarthy JEG, Brimacombe R (1994) Prokaryotic translation: the interactive pathway leading to initiation. Trends in Genet 10:402–407
Mogridge J, Greenblatt J (1998) Specific binding of Escherichia coli ribosomal protein S1 to boxA transcriptional terminator RNA. J Bacteriol 180:2248–2252
Nagaya S, Kawamura K, Shinmyo A, Kato K (2010) The HSP terminator of Arabidopsis thaliana increases gene expression in plant cells. Plant Cell Physiol 51:328–332
Nakamoto T (2009) Evolution and the universality of the mechanism of initiation of protein synthesis. Gene 432:1–6
Nakamoto T (2011) Mechanisms of the initiation of protein synthesis: in reading frame binding of ribosomes to mRNA. Mol Biol Rep 38:847–855
Ninfa AJ, Jiang P (2005) PII signal transduction proteins: sensors of α-ketoglutarate that regulate nitrogen metabolism. Curr Opin Microbiol 8:168–173
Nunes-Nesi A, Fernie AR, Stitt M (2010) Metabolic and signaling aspects underpinning the regulation of plant carbon nitrogen interactions. Mol Plant 3:973–996
Orom UA, Nielsen FC, Lund AH (2008) MicroRNA-10a binds the 5′UTR of ribosomal protein mRNAs and enhances their translation. Mol Cell 30:460–471
Ortega JL, Roche D, Sengupta-Gopalan C (1999) Oxidative turnover of soybean root glutamine synthetase: in vitro and in vivo studies. Plant Physiol 119:1483–1495
Ortega JL, Temple SJ, Bagga S, Sengupta-Gopalan C (2001) Constitutive over-expression of cytosolic glutamine synthetase (GS1) genes in transgenic alfalfa demonstrates that GS1 may be regulated both at the level of RNA and protein turnover. Plant Physiol 126:109–121
Ortega JL, Moguel-Esponda S, Potenza C, Conklin CF, Quintana A, Sengupta-Gopalan C (2006) The 3′ untranslated region of a soybean cytosolic glutamine synthetase (GS1) affects transcript stability and protein accumulation in transgenic alfalfa. Plant J 45:842–846
Roberts CS, Rajagopal S, Smith LA, Nguyen TA, Yang W, Nugroho S, Ravi KS, Cao ML, Vijayachandra K, Patell V, Harcourt RL, Dransfield L, Desamero N, Slamet I, Keese P, Kilian A, Jefferson RA (1998) A comprehensive set of modular vectors for advanced manipulations and efficient transformation of plants by both Agrobacterium and direct DNA uptake methods. pCAMBIA vector release manual version 3.05. CAMBIA. Canberra, Australia
Rogers SG, Klee HJ, Horsch RB, Fraley RT (1987) Improved vectors for plant transformation: expression cassette vectors and new selectable markers. Methods Enzymol 153:253–277
Sakakibara H, Shimizu H, Hase T, Yamazaki Y, Takao T, Shimonishi Y, Sugiyama T (1996) Molecular identification and characterization of cytosolic isoforms of glutamine synthetase in maize roots. J Biol Chem 271:29561–29568
Satoh J, Kato K, Shinmyo A (2004) The 5′-untranslated region of the tobacco alcohol dehydrogenase gene function as an effective translational enhancer in plant. J Biosci Bioeng 98:1–8
Seabra AR, Vieira CP, Cullimore JV, Carvalho HG (2010) Medicago truncatula contains a second gene encoding a plastid located glutamine synthetase exclusively expressed in developing seeds. BMC Plant Biol 10:183
Simon B, Sengupta-Gopalan C (2010) The 3′ untranslated region of the two cytosolic glutamine synthetase (GS1) genes in alfalfa (Medicago sativa) regulates transcript stability in response to glutamine. Planta 232:1151–1162
Smith CA, Weljie AM, Moorhead GBG (2003) Molecular properties of the putative nitrogen sensor PII from Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 33:353–360
Stupina VA, Yuan X, Meskauskas A, Dinman JD, Simon AE (2011) Ribosome binding to a 5′ translational enhancer is altered in the presence of the 3′ untranslated region in Cap-independent translation of Turnip Crinkle Virus. J Virol 85:4638–4653
Tzeng TY, Kong LR, Chen CH, Shaw CC, Yang CH (2009) Overexpression of the lily p70s6k gene in Arabidopsis affects elongation of flower organs and indicator TOR-dependent regulation of AP3, PI and SUP translation. Plant Cell Physiol 50:1695–1709
Wang CT, Xu YN (2010) The 5′ untranslated region of the FAD3 mRNA is required for its translational enhancement at low temperature in Arabidopsis roots. Plant Sci 179:234–240
Wang R, Guan P, Chen M, Xing X, Zhang Y, Crawford NM (2010) Multiple regulatory elements in the Arabidopsis NIA1 promoter act synergistically to form a nitrate enhancer. Plant Physiol 154:423–432
Zou Z, Eibil C, Koop HU (2003) The stem-loop region of the tobacco psbA 5′UTR is an important determinant of mRNA stability and translation efficiency. Mol Genet Genomics 269:340–349
Zuker M (1989) On finding all suboptimal foldings of an RNA molecule. Science 244:48–52
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health (Grant number S06 GM08136-32), by the US Department of Agriculture (Grant number 2007-03596), and by the Agricultural Experimental Station at New Mexico State University. We thank Dr. Suman Bagga and Dr. Laura Rodriguez-Uribe for their helpful comments on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by H. Ronne.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ortega, J.L., Wilson, O.L. & Sengupta-Gopalan, C. The 5′ untranslated region of the soybean cytosolic glutamine synthetase β1 gene contains prokaryotic translation initiation signals and acts as a translational enhancer in plants. Mol Genet Genomics 287, 881–893 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-012-0724-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-012-0724-6