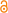ハプログループD (Y染色体)
出典: フリー百科事典『ウィキペディア(Wikipedia)』 (2024/03/22 21:18 UTC 版)
ハプログループD (Y染色体)(ハプログループD (Yせんしょくたい)、英: Haplogroup D (Y-DNA))とは、分子人類学で用いられる、人類のY染色体ハプログループ(型集団)の分類で、YAPと呼ばれる変異の型を持つもののうちの「CTS3946」に定義されるものである。
- ^ a b c d e f Haber M, Jones AL, Connell BA, Arciero E, Yang H, Thomas MG, Xue Y, Tyler-Smith C (August 2019). “A Rare Deep-Rooting D0 African Y-Chromosomal Haplogroup and Its Implications for the Expansion of Modern Humans Out of Africa”. Genetics 212 (4): 1421–1428. doi:10.1534/genetics.119.302368. PMC 6707464. PMID 31196864.
- ^ Cabrera, Vicente M.; Rodriguez, Julia Patricia Marrero; Abu-Amero, Khaled K.; Larruga, Jose M. (2017-12-13). “Carriers of mitochondrial DNA macrohaplogroup L3 basic lineages migrated back to Africa from Asia around 70,000 years ago.” (英語). bioRxiv: 233502. doi:10.1101/233502.
- ^ a b アンダマン諸島については、従来よりハプログループD-M174*(xD-M15,D-M55)が高頻度であるとのデータ(kumarasamy et al. 2003)があり、その後系統解析の研究の進展によりアンダマン諸島のD-M174*はD-Y34537であることがわかった(Y-Full)。
- ^ Mondal, M., Bergström, A., Xue, Y. et al. Y-chromosomal sequences of diverse Indian populations and the ancestry of the Andamanese. Hum Genet 136, 499–510 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-017-1800-0
- ^ a b c Shi, Hong; Zhong, Hua; Peng, Yi; Dong, Yong-li; Qi, Xue-bin; Zhang, Feng; Liu, Lu-Fang; Tan, Si-jie et al. (October 29, 2008). “Y chromosome evidence of earliest modern human settlement in East Asia and multiple origins of Tibetan and Japanese populations”. BMC Biology (BioMed Central) 6: 45. doi:10.1186/1741-7007-6-45. PMC 2605740. PMID 18959782 2018年8月4日閲覧。.
- ^ Weale ME, Shah T, Jones AL et al. (September 2003). "Rare deep-rooting Y chromosome lineages in humans: Lessons for Phylogeography". Genetics 165 (1): 229–34. PMC 1462739. PMID 14504230.
- ^ Weale ME, Shah T, Jones AL et al. (September 2003). "Rare deep-rooting Y chromosome lineages in humans: Lessons for Phylogeography". Genetics 165 (1): 229–34. PMC 1462739. PMID 14504230.
- ^ a b Estes, Roberta (2019年6月21日). “Exciting New Y DNA Haplogroup D Discoveries!” (英語). DNAeXplained - Genetic Genealogy. 2019年7月8日閲覧。
- ^ 崎谷満『DNA・考古・言語の学際研究が示す新・日本列島史』(勉誠出版 2009年)
- ^ Cabrera, Vicente M.; Rodriguez, Julia Patricia Marrero; Abu-Amero, Khaled K.; Larruga, Jose M. (2017-12-13). “Carriers of mitochondrial DNA macrohaplogroup L3 basic lineages migrated back to Africa from Asia around 70,000 years ago.” (英語). bioRxiv: 233502. doi:10.1101/233502.
- ^ Veeramah RK, Connell AB, Pour AN, Powell A, Plaster AC, Zeitlyn D, Mendell RN, Weale EM, Bradman N, Thomas GM (2010). “Little genetic differentiation as assessed by uniparental markers in the presence of substantial language variation in peoples of the Cross River region of Nigeria”. BMC Evolutionary Biology 10: 1–17. doi:10.1186/1471-2148-10-92. PMC 2867817. PMID 20356404.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Hammer MF, Karafet TM, Park H et al. (2006). "Dual origins of the Japanese: common ground for hunter-gatherer and farmer Y chromosomes". J. Hum. Genet. 51 (1): 47–58. doi:10.1007/s10038-005-0322-0. PMID 16328082.
- ^ Su, Bing; Xiao, Chunjie; Deka, Ranjan; Seielstad, Mark T.; Kangwanpong, Daoroong; Xiao, Junhua; Lu, Daru; Underhill, Peter et al. (2000). “Y chromosome haplotypes reveal prehistorical migrations to the Himalayas”. Human Genetics 107 (6): 582–90. doi:10.1007/s004390000406. PMID 11153912.
- ^ Cordaux, R.; Weiss, G; Saha, N; Stoneking, M (2004). “The Northeast Indian Passageway: A Barrier or Corridor for Human Migrations?”. Molecular Biology and Evolution 21 (8): 1525–33. doi:10.1093/molbev/msh151. PMID 15128876.
- ^ Chandrasekar, A.; Saheb, S. Y.; Gangopadyaya, P.; Gangopadyaya, S.; Mukherjee, A.; Basu, D.; Lakshmi, G. R.; Sahani, A. K. et al. (2007). “YAP insertion signature in South Asia”. Annals of Human Biology 34 (5): 582–6. doi:10.1080/03014460701556262. PMID 17786594.
- ^ Reddy BM, Langstieh BT, Kumar V, Nagaraja T, Reddy ANS et al. (2007). Awadalla, Philip. ed. “Austro-Asiatic Tribes of Northeast India Provide Hitherto Missing Genetic Link between South and Southeast Asia”. PLoS ONE 2 (11): e1141. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0001141. PMC 2065843. PMID 17989774.
- ^ D-M15以外のマーカーについては検査されていない。
- ^ Wen B, Xie X, Gao S, et al. Analyses of genetic structure of Tibeto-Burman populations reveals sex-biased admixture in southern Tibeto-Burmans. Am J Hum Genet. 2004;74(5):856-865. doi:10.1086/386292
- ^ Tatiana Karafet, Liping Xu, Ruofu Du, William Wang, Shi Feng, R. S. Wells, Alan J. Redd, Stephen L. Zegura, and Michael F. Hammer, "Paternal Population History of East Asia: Sources, Patterns, and Microevolutionary Processes." American Journal of Human Genetics 69: 615–628, 2001.
- ^ Yali Xue, Tatiana Zerjal, Weidong Bao, Suling Zhu, Qunfang Shu, Jiujin Xu, Ruofu Du, Songbin Fu, Pu Li, Matthew E. Hurles, Huanming Yang, and Chris Tyler-Smith, "Male Demography in East Asia: A North–South Contrast in Human Population Expansion Times." Genetics 172: 2431–2439 (April 2006).
- ^ Genetic origin of Kadai-speaking Gelong people on Hainan island viewed from Y chromosomes
- ^ a b Shi Yan, Chuan-Chao Wang, Hui Li, Shi-Lin Li, Li Jin, and The Genographic Consortium, "An updated tree of Y-chromosome Haplogroup O and revised phylogenetic positions of mutations P164 and PK4." European Journal of Human Genetics (2011) 19, 1013–1015.
- ^ Kumarasamy Thangaraj, Lalji Singh, Alla G. Reddy, V.Raghavendra Rao, Subhash C. Sehgal, Peter A. Underhill, Melanie Pierson, Ian G. Frame, Erika Hagelberg(2003);Genetic Affinities of the Andaman Islanders, a Vanishing Human Population ;Current Biology Volume 13, Issue 2, 21 January 2003, Pages 86–93 doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(02)01336-2
- ^ “East Asian ancestry in India”. 2015年1月閲覧。
- ^ Carlhoff, Selina; Duli, Akin; Nägele, Kathrin; Nur, Muhammad; Skov, Laurits; Sumantri, Iwan; Oktaviana, Adhi Agus; Hakim, Budianto et al. (2021). “Genome of a middle Holocene hunter-gatherer from Wallacea”. Nature 596 (7873): 543–547. doi:10.1038/s41586-021-03823-6. ISSN 0028-0836. PMC 8387238. PMID 34433944.
- ^ “D Haplogroup (Y-DNA) Project”. FAMILY TREE DNA (2013年6月1日). 2013年10月19日閲覧。
- ^ 田島等の2004年の論文"Genetic Origins of the Ainu inferred from combined DNA analyses of maternal and paternal lineages"による
- ^ a b c d e YOUICHI SATO, TOSHIKATSU SHINKA, ASHRAF A. EWIS, AIKO YAMAUCHI, TERUAKI IWAMOTO, YUTAKA NAKAHORI Overview of genetic variation in the Y chromosome of modern Japanese males., doi:10.1537/ase.140709
- ^ a b c Nonaka, I.; Minaguchi, K.; Takezaki, N. (February 2, 2007). “Y-chromosomal Binary Haplogroups in the Japanese Population and their Relationship to 16 Y-STR Polymorphisms”. Annals of Human Genetics (John Wiley & Sons) 71 (Pt 4): 480–95. doi:10.1111/j.1469-1809.2006.00343.x. PMID 17274803.
- ^ Peter A. Underhill, Peidong Shen, Alice A. Lin, et al., "Y chromosome sequence variation and the history of human populations." Nature Genetics, Volume 26, November 2000.
- ^ Toshikatsu Shinka, Keiko Tomita, Tatsushi Toda, Svetlana E. Kotliarova, Juwon Lee, Yoko Kuroki, Dong Kyu Jin, Katsushi Tokunaga, Hideki Nakamura, and Yutaka Nakahori, "Genetic variations on the Y chromosome in the Japanese population and implications for modern human Y chromosome lineage." Journal of Human Genetics (1999) 44: 240-245.
- ^ a b Shoji Totsuka, The Super Science High School Consortium, Youichi Sato, and Masashi Tanaka, "A study of the geographic distribution of Y chromosomal and mitochondrial DNA haplogroups in Japanese population by Super Science High School Consortium (SSH)." Anthropological Science (Japanese Series) Vol. 124(2), 85–91, 2016.
- ^ Matthew C. Dulik, Sergey I. Zhadanov, Ludmila P. Osipova, et al. (2012), "Mitochondrial DNA and Y Chromosome Variation Provides Evidence for a Recent Common Ancestry between Native Americans and Indigenous Altaians." The American Journal of Human Genetics 90, 229–246, February 10, 2012. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.12.014.
- ^ Kharkov, V. N.; Stepanov, V. A.; Medvedeva, O. F.; Spiridonova, M. G.; Voevoda, M. I.; Tadinova, V. N.; Puzyrev, V. P. (2007). “Gene pool differences between Northern and Southern Altaians inferred from the data on Y-chromosomal haplogroups”. Russian Journal of Genetics 43 (5): 551–562. doi:10.1134/S1022795407050110.
- ^ Tajima,A. et al. (2004). "Genetic origins of the Ainu inferred from combined DNA analyses of maternal and paternal lineages". Journal of Human Genetics 49 (4): 187–193.
- ^ Y-DNA Haplogroup D and its Subclades - 2019
- ^ Y-DNA Haplogroup D and its Subclades - 2014
- 1 ハプログループD (Y染色体)とは
- 2 ハプログループD (Y染色体)の概要
- 3 下位系統の頻度
- 4 参考文献
- ハプログループD_(Y染色体)のページへのリンク