ドパミンは神経伝達物質の一つで、カテコールアミンと呼ばれる種類に属します。アミノ酸のチロシンから酵素の働きによって合成されます。ドパミンが働く主な神経経路には黒質線条体路、中脳辺縁系路、中脳皮質路の3つがあります。黒質線条体路はパーキンソン病と関連し、中脳辺縁系路と中脳皮質路は統合失調症と関連するとされています。アルコールを飲むことによって快く感じるのは脳内の報酬系と呼ばれる神経系が活性化するためと考えられますが、この報酬系ではドパミンが中心的な役割を果たしています。アルコール、麻薬、覚せい剤などの依存を形成する薬物の多くはドパミンを活発にする作用があり、そのために報酬系が活性化するので、これらの薬物を使用すると快感をもたらすと考えられます。
ドーパミン
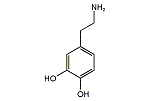
| 分子式: | C8H11NO2 |
| その他の名称: | ドーパミン、3-ヒドロキシチラミン、3,4-ジヒドロキシフェネチルアミン、Dopamine、3-Hydroxytyramine、3,4-Dihydroxyphenethylamine、3,4-Dihydroxybenzeneethanamine、ドパミン、4-(2-Aminoethyl)pyrocatechol、4-(2-Aminoethyl)-1,2-benzenediol、4-(2-Aminoethyl)benzene-1,2-diol、4-(2-Aminoethyl)catechol |
| 体系名: | 2-(3,4-ジヒドロキシフェニル)エチルアミン、3,4-ジヒドロキシベンゼンエタンアミン、4-(2-アミノエチル)-1,2-ベンゼンジオール、4-(2-アミノエチル)ピロカテコール、4-(2-アミノエチル)ベンゼン-1,2-ジオール、4-(2-アミノエチル)カテコール |
ドーパミン
(ドパミン から転送)
出典: フリー百科事典『ウィキペディア(Wikipedia)』 (2023/10/23 09:55 UTC 版)
ドーパミン(英: dopamine)は、中枢神経系に存在する神経伝達物質で、アドレナリン、ノルアドレナリンの前駆体でもある。運動調節、ホルモン調節、快の感情、意欲、学習などに関わる。セロトニン、ノルアドレナリン、アドレナリン、ヒスタミン、ドーパミンを総称してモノアミン神経伝達物質と呼ぶ。またドーパミンは、ノルアドレナリン、アドレナリンと共にカテコール基をもつためカテコールアミンとも総称される。医学・医療分野では日本語表記をドパミンとしている[1]。合成された注射製剤が循環器科[2]、救急[3]、集中治療医学[2]、麻酔科学[4]等の領域で頻用されている。
- ^ 日本神経学会用語委員会編『神経学用語集 改訂第3版』文光堂、2008年、p.42
- ^ a b Suzuki, Reina; Uchino, Shigehiko; Sasabuchi, Yusuke; Kawarai Lefor, Alan; Sanui, Masamitsu (2022-04-02). “Dopamine use and its consequences in the intensive care unit: a cohort study utilizing the Japanese Intensive care PAtient Database”. Critical Care 26 (1): 90. doi:10.1186/s13054-022-03960-y. ISSN 1364-8535. PMC PMC8977005. PMID 35366934.
- ^ RaaeNielsen, Jen; Fales, William (2017-01-01). “Use of Dopamine in a Statewide Emergency Medical Services System”. Research Day.
- ^ “麻酔薬および麻酔関連薬使用ガイドライン 第3版 Ⅶ 循環作動薬”. 公益社団法人日本麻酔科学会. p. 231. 2023年9月23日閲覧。
- ^ HARVARD MEDICAL SCHOOL (2016年10月). “Need to remember something? Exercise four hours later”. 2017年9月2日閲覧。
- ^ Sogawa R, Shimomura Y, Minami C, Maruo J, Kunitake Y, Mizoguchi Y, Kawashima T, Monji A, Hara H. (2016-8). “Aripiprazole-Associated Hypoprolactinemia in the Clinical Setting.”. en:Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology. 36 (4): 385-7. doi:10.1097/JCP.0000000000000527. PMID 27281387.
- ^ Vrignaud L, Aouille J, Mallaret M, Durrieu G, Jonville-Béra AP. (2014-11-1). “Hypersexuality associated with aripiprazole: a new case and review of the literature.”. Therapie. 69 (6): 525-527. doi:10.2515/therapie/2014064. PMID 25293487.
- ^ FDA Drug Safety Communication: FDA warns about new impulse-control problems associated with mental health drug aripiprazole (Abilify, Abilify Maintena, Aristada) (05-03-2016 FDA)
- ^ Broadley KJ (March 2010). “The vascular effects of trace amines and amphetamines”. Pharmacol. Ther. 125 (3): 363–375. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2009.11.005. PMID 19948186.
- ^ “A renaissance in trace amines inspired by a novel GPCR family”. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 26 (5): 274–281. (May 2005). doi:10.1016/j.tips.2005.03.007. PMID 15860375.
- ^ “The endogenous substrates of brain CYP2D”. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 724: 211–218. (February 2014). doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.12.025. PMID 24374199. "The highest level of brain CYP2D activity was found in the substantia nigra ... The in vitro and in vivo studies have shown the contribution of the alternative CYP2D-mediated dopamine synthesis to the concentration of this neurotransmitter although the classic biosynthetic route to dopamine from tyrosine is active. ... Tyramine levels are especially high in the basal ganglia and limbic system, which are thought to be related to individual behavior and emotion (Yu et al., 2003c). ... Rat CYP2D isoforms (2D2/2D4/2D18) are less efficient than human CYP2D6 for the generation of dopamine from p-tyramine. The Km values of the CYP2D isoforms are as follows: CYP2D6 (87–121 μm) ≈ CYP2D2 ≈ CYP2D18 > CYP2D4 (256 μm) for m-tyramine and CYP2D4 (433 μm) > CYP2D2 ≈ CYP2D6 > CYP2D18 (688 μm) for p-tyramine"
- ^ Lin Zhang, Yukihiko Shirayama, Masaomi Iyo, Kenji Hashimoto. (2007-9). “Minocycline attenuates hyperlocomotion and prepulse inhibition deficits in mice after administration of the NMDA receptor antagonist dizocilpine.”. en:Neuropsychopharmacology (journal). 32 (9). doi:10.1038/sj.npp.1301313. PMID 17228338.
- 1 ドーパミンとは
- 2 ドーパミンの概要
- 3 概要
- 4 生合成過程
- 5 関連項目
「ドパミン」の例文・使い方・用例・文例
ドパミンと同じ種類の言葉
固有名詞の分類
- ドパミンのページへのリンク